- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Woman Discovers She Was 4 Months Pregnant Days After Giving Birth—Doctor Explains How
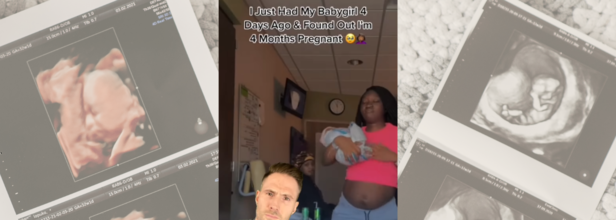
Credits: Instagram & Canva
Dr Joe Whittington, who goes by Dr Joe on his social media platforms is a certified MD in Emergency Medicine based in Apple Valley, California is a social media medical educator. He uploads many real-life health-related stories and cases to educate general public about it. In one such videos, he featured a woman who just had her baby four days ago and found out that she was four months pregnant.
Is This Possible?
Dr Joe says, "technically, yes". This phenomenon is known as superfetation that occurs when a woman releases an egg and it gets fertilized and implanted after she is already pregnant.
He says, "Usually pregnancy changes such as hormonal changes, changes in the uterus, and the cervical mucous plug all work to prevent this. So superfetation is extremely rare with only about 10 documented cases. But, it is possible."
What Is Superfetation?
It is a rare phenomenon where a second pregnancy occurs alongside an existing one. This happens when another ovum or the egg is fertilized by sperm and implanted in the womb days or weeks later than the first one. Babies born from superfetation are often considered twins as they may be born on the same birth on the same day. However, not always does it happen. In the case that Dr Joe picked up, the baby had a difference of four months.
ALSO READ: Pregnancy Trimesters, Everything You Need To Know About It
So, How Does It Happen?
In humans, pregnancy occurs when an egg is fertilized by sperm and implants in the uterus. For superfetation to happen, a second egg must be fertilized and implanted separately while a pregnancy is already underway.
For this to occur, three highly unlikely events must take place:
Ovulation during an ongoing pregnancy – This is rare because pregnancy hormones typically prevent further ovulation.
Fertilization of the second egg – Once pregnant, a woman’s cervix forms a mucus plug that blocks sperm from entering, making fertilization extremely unlikely.
Implantation in an already pregnant uterus – Implantation requires specific hormonal changes that usually don’t occur once pregnancy has begun.
Additionally, a growing fetus takes up space, making it harder for another embryo to implant.
Because these conditions are so improbable, superfetation is considered nearly impossible in natural pregnancies. However, a few reported cases exist, primarily in women undergoing fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF). In such cases, an embryo is transferred into the uterus, but if ovulation unexpectedly occurs and the egg is fertilized, superfetation might happen a few weeks later.
Could There Be Any Complications?
The biggest complication with superfetation is premature birth. The baby maybe born before time and could have the following medical conditions:
- trouble breathing
- low birth weight
- movement and coordination problems
- difficulties with feeding
- brain hemorrhage or bleeding in the brain
- neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, which is a breathing disorder caused by underdeveloped lungs
Women too could have complication, which includes high blood pressure and protein in the urine, a condition called preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes.
Karnataka’s Social Media Ban To Help Children Find Life Beyond Screens

Credit: Canva
Chief Minister Siddaramaiah’s announcement during his presentation of the Karnataka State Budget 2026-27, proposing a ban on social media for children under 16 years of age, has sparked intense interest among parents and professionals alike. As the first state in India to attempt such a sweeping measure, the government has invited us to reflect upon this proposal.
We are in an age where technological advancements have blurred the lines between online and offline worlds, blending them seamlessly. While this is the norm in the world of adults, it has silently reshaped childhood with increased screentime.
Concerns about digital dependency, anxiety disorders in children, and reduced focus in academic and non-academic tasks have already made it to research papers and therapy rooms.
But Karnataka has now shifted the focus from debate to discussion and action. While a ban may reduce certain risks of social media exposure, children’s psychological needs like social connection, belonging, peer group and individual identity, besides guidance, must be nurtured if such protections are to be meaningful.
The Pediatric Perspective: A Medical Minefield
From a psychological perspective, the idea of an age-based social media ban is both promising and complex. On the brighter side, reducing screen usage can help address problems of poor sleep schedules, heightened anxiety, and trouble concentrating in studies or tasks. These problems have become increasingly common among not only adolescents, but very young children too.
However, age alone cannot be used as the single measure of readiness to implement this proposal. Two children of the same age may differ vastly in maturity levels, coping skills, and the ability to use technology responsibly.
The deeper issue is not simply “how much time” children spend online, but “what they do there”. Creative exploration, learning, and connection can be enriching, while endless scrolling reinforces dependency and stress.
A ban can reduce such harmful patterns, but in order to have real impact, such a move should be paired with support for children’s psychological needs to help them combat loneliness, handle peer pressure, and guiding their search for identity. Addressing these issues along with the ban can make the protection well intended, more meaningful and long-lasting.
The Silent Crisis: Nocturnal Anxiety And Doom-scrolling
Late-night scrolling (doom scrolling) is more than just a disruption of sleep. It is a psychological trigger for worry and overthinking. In the quiet of the night, children are left alone with a flood of unfiltered information, which can heighten anxiety, and unwanted exposure to inappropriate content.
An effective way to combat the dangers of unsupervised social media access could be “digital sundowning” i.e. setting clear screen time guidelines for children. Families can create screen-free zones, especially in bedrooms, bathrooms, and at dining tables, or create “phone parking zones” – a specific place in the house to keep all phones so no one is carrying them around all the time. This can encourage children towards healthier routines.
Unlike government-imposed bans, household practices can set healthy and firm boundaries, reinforce self-regulation and reduce the anxiety that comes from constant connectivity and information overload.
Symptoms In The Clinic: Beyond The Screen
In therapy rooms and schools, counsellors are addressing more and more concerns about children and adolescents spending excessive time with their screens. Some of the common ones are highlighted here:
- Social Isolation in Hyper Connectivity: Children may appear socially active online but withdraw from face-to-face interactions, leaving them paradoxically isolated.
- Body Image Concerns: Exposure to curated images on social media can fuel anxiety about appearance among growing children, who are already socially awkward during adolescence. This goes beyond normal teenage insecurity and can spiral into unhealthy self-image or self-criticism.
- Academic Fatigue: Digital content trains the brain to expect constant novelty and quick changes within a short time span of seconds or minutes, which makes textbooks and traditional classroom driven problem-solving feel slow and tiring. This leads to academic fatigue, where children struggle to sustain focus for deeper learning.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Constant checking of devices reflects a deep-seated need for validation and belonging. FOMO keeps children’s nervous systems on a constant loop of high alert, thus undermining emotional stability.
What Comes Next: The Prioritization Framework
For this ban to have a lasting impact, it needs to draw on psychological principles. Restrictions work best when paired with meaningful alternatives, as children are known to engage positively when they feel supported rather than restricted or scolded. A framework needs to be set up where learning and guidance is prioritized and alternatives offered are strengthened. Some pointers:
Digital Literacy in Schools: Children should be taught not only to limit screen time but also to understand how online platforms work. Lessons on algorithms, advertising, and curated content help them understand and evaluate what they see, so they become more resilient to digital influence.
Parental Guidance Programs: As with other trained behaviors, parents play a central role in shaping healthy digital habits too. Guidance programs can provide resources and strategies for families to showcase balanced device use. When adults demonstrate mindful online usage and behavior, children are likely to follow.
Physical and Social Alternatives: If digital spaces are restricted, offline opportunities must be strengthened. Sports, arts, and community activities help children gain a sense of belonging and enjoyment beyond screens, thus building confidence and social skills in real life.
Collaboration with Tech Companies: Lasting change requires cooperation of technology providers and social media platforms. Stricter age verification systems and design changes at the source are needed, rather than placing usage responsibility on children. By remodeling platforms, risk of unsupervised penetration of digital content can be mitigated so children may still be allowed safe, and age appropriate engagement on social media.
As Karnataka moves into this new territory, one thing is certain – the intention is noble. However, the execution of such a ban will require a fine balance of protection and empowerment, as it attempts to re-imagine childhood experiences in an age where the “virtual” and the “real” are meshed together. Whether this becomes a guiding model for the rest of the country, will depend entirely on how thoughtfully it is carried out.
Karnataka’s proposed ban is a bold first step, but its true impact will depend on how parents, teachers, and policymakers align on this, because healthy childhoods thrive not on restrictions, but through resilience, support, guidance, and strong offline connections that nurture growth and belonging.
Giant 99th Percentile Baby Of 5.9Kg Born In New York Has Taken The Internet By Storm

Credits: Canva
A giant baby weighing 5.9 kg was born to a mother in New York. She was left in shock and amaze when she saw that she had delivered a boy much bigger than she expected. The newborn baby weighed almost twice as much as an average baby. The baby is born to Terrica and Shawn on January 31 in Cayuga Medical Center. His weigh has made him the heaviest baby ever born at the Ithaca-based hospital, reported the NY Post.
The mother of four said she knew her son would be a little heavy, however did not know he would be this big. She said he is already wearing three-to-six month old baby clothes and diaper. She feels like she has given birth to a three-month-old.
The hospital also posted a photo of the baby on Facebook, comparing him with another newborn baby alongside. The other baby too was born on the same day, whose name is Margot and weighs only 1.8 kg.
Robyn Torgalski, System Director of Maternal and Child Health at Centralus Health, described the two births as a powerful reminder that every newborn and every birth story is unique. She noted that whether a baby weighs four pounds or thirteen, the medical team is fully equipped to deliver the highest level of care to both mother and child. Torgalski added that she is proud of the maternity services at Cayuga Health and feels privileged to support families during such an important life event.
Read: 99th Percentile Baby: What It Means, Risks, And What Parents Should Know
Giant Babies: All About Them
As per the Guinness World Records, the heaviest recorded baby ever was 9.97 kg born in Italy in 1955.
Dr Sermed Mezher, a digital health content creator, and a London based GP, shared: "Babies in the womb who measure in the 99th percentile for weight are referred to as macrosomic baby, meaning they are significantly larger than average for their gestational age. While most macrosomic babies are healthy, their larger size can increase the risk of certain complications during pregnancy and delivery."
What Does It Mean To Be A 99th Percentile Baby?
Babies in the 99th percentile for weight are larger than 99% of babies at the same gestational age. This may lead to birth complications such as shoulder dystocia—when the baby’s shoulders become stuck during delivery—or increase the likelihood of cesarean section. Mothers may also experience a higher risk of perineal tearing, postpartum hemorrhage, and greater pregnancy weight gain. Contributing factors include maternal diabetes, genetics, or excess weight gain during pregnancy.
This larger birth size is medically categorized under fetal macrosomia, which refers to babies in the top 10% of weight for gestational age—with the 99th percentile representing the most extreme cases.
What Causes A Baby To Be a 99th Percentile Baby?
While we do not know the cause in this case, there are certain reason a baby may fall into the category, which includes:
- You have a large fundal height (a measurement of fetal growth)
- Significant weight gain during pregnancy
- Gestational diabetes or pre-existing diabetes
- History of delivering large babies
- Prolonged pregnancy past due date
- Parental genetics (you were a large baby yourself)
Rare Brain Surgery In 2.5-Year-Old Helps Reverse Devastating Stroke Effects
Credit: Canva
A team of doctors in Uttar Pradesh successfully performed a rare and highly complex neuro-interventional procedure on a two-and-a-half-year-old girl that enabled significant neurological recovery.
The child initially had severe indigestion and mild fever. However, it quickly escalated into repeated seizures, altered sensorium, and sudden loss of movement.
At ApolloMedics Super Speciality Hospital, Lucknow, the child was diagnosed with deep Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST) with multiple brain infarcts -- a condition associated with high mortality risk and potentially devastating long-term neurological disability.
“Deep cerebral venous thrombosis in toddlers is exceptionally rare, and neuro-intervention in pediatric stroke is particularly challenging because of the small size of vessels and increased risk of bleeding,” said Dr. Dewansh Mishra, Interventional Neuro-Radiologist, at ApolloMedics.
“Literature on catheter-directed thrombolysis in such young patients is limited. In this case, the child was deteriorating quickly, and timely escalation to precision neuro-intervention was crucial to prevent irreversible brain injury and give her the best possible chance of recovery,” he added.
The Rare Brain Surgery
Dr. Mishra said that the child was also diagnosed with Antiphospholipid Antibody (APLA) syndrome, a clotting disorder that increases the tendency of blood to clot excessively.
Infection and dehydration further worsened the condition and accelerated stroke progression.
Recognizing the urgency, a multidisciplinary team of doctors took a critical, high-risk decision to escalate treatment without delay. They performed intracranial catheter-directed thrombolysis, under general anesthesia, preventing irreversible brain injury in the toddler.
Through the femoral vein in the thigh, a microcatheter was carefully navigated into the intracranial venous system, and clot-dissolving medication was delivered directly at the site of thrombosis to restore venous drainage. This was successful in limiting further neurological damage.
"After nearly three weeks of intensive care and rehabilitation, the child was discharged with significant neurological recovery. She is now able to walk, speak, and perform activities that children of her age do," the hospital said in a statement.
The case, marked by rapid deterioration and a narrow window for intervention, will be presented at the Indian National Stroke Conference 2026 in Kochi, underlining both its clinical significance and the growing capabilities of advanced stroke care in India.
Can Stroke Occur In Very Young Children?
While stroke is more common in adults than in children, the condition can occur in children and debilitate their lives.
Pediatric stroke is a rare condition affecting one in every 4,000 newborns and an additional 2,000 older children each year.
Stroke in young children is similar to that of adults and is caused by a brain injury due to the interruption of blood flow to part of the brain.
In young children, the diagnosis is often delayed. A stroke typically begins suddenly in children and infants, with Seizures the most common symptom.
Extreme sleepiness or altered mental status and a tendency to use only one side of the body are other major symptoms.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

