Credits: Canva
The Blue Zones: What We Can Learn from the World’s Longest-Lived People
"Blue Zones" are geographic areas with lower rates of chronic diseases and longer life expectancy. This is possible because of their diet, fasting, exercise, along with other factors. This term was first used by author Dan Buettner, who studied the areas of the world where people lived exceptionally long lives. He called them the "Blue zones", because when Buettner and his colleagues were searching for these areas, they drew it with a blue circles around them on the map.
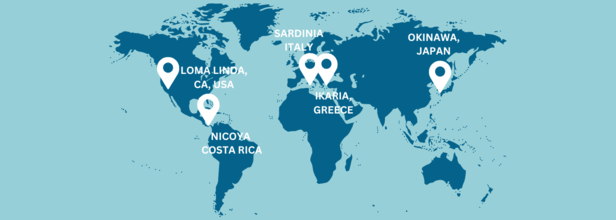
Buettner in his book described these "Blue Zones" in five regions:
- Icaria (Greece)
- Ogliastra, Sardania (Italy)
- Okinawa (Japan)
- Nicoya Peninsula (Costa Rica)
- The Seventh-day Adventists in Loma Linda, California (USA)
What can be learned from the Blue Zones?
The study that Buettner and Sam Skemp published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, which is also found on the online portal of National Library of Medicine, under the National Center for Biotechnology Information, mentions lessons learned from these zones:
Moving Naturally: The study mentions that the world’s longest-lived people do not pump iron, run marathons, or join gyms. Instead, they live in environments that constantly nudge them into moving without thinking about it. They grow gardens and do not have mechanical conveniences for house and yard work.
Purpose: Ikigai, do we, by now, not know about it? The concept reached its peak of fame by a book, which Okinawans mean the "purpose", whereas the Nicoyans call it plan de vida. The study mentions, for both, it translates to “why I wake up in the morning.” Knowing your sense of purpose is worth up to 7 years of extra life expectancy."
Downshift: Everyone experiences stress, even the people in blue zones too. Stress leads to chronic inflammation, associated with every major age-related disease. What the world’s longest-lived people have that others do not are routines to shed that stress. Okinawans take a few moments each day to remember their ancestors; Adventists pray; Ikarians take a nap; and Sardinians do happy hour.
80% Rule: Hara Hachi bu - is an Okinawan mantra, founded 2500-year ago by Confucianism. It is said before the meal to remind people to stop eating when they are stomach are 80% full. The study mentions that the "20% gap between not being hungry and feeling full could be the difference between losing weight or gaining it." The study also found that the people in the Blue Zones eat their smallest meal in the late afternoon or early evening, and then, they do not eat any more the rest of the day.
Plant slant: The people of blue zones mostly eat a plant-based diet and meat is only eaten on an average of 5 times per month. Serving sizes are 3 to 4 oz, about the size of a deck of cards.
Wine @ 5: The study mentions: "People in all Blue Zones (except Adventists) drink alcohol moderately and regularly. Moderate drinkers outlive nondrinkers. The trick is to drink 1 to 2 glasses per day (preferably Sardinian Cannonau wine), with friends and/or with food. And no, you cannot save up all week and have 14 drinks on Saturday."
Belong: All but 5 of the 263 centenarians interviewed belonged to some faith-based community. The study mentions that there is research that backs up that attending faith-based services 4 times per month adds 4 to 14 years of life expectancy.
Loved ones first: All these people put their family first. It means to love their ageing parents, grand parents and committing to one life partner, which can add up to 3 years of life expectancy.
Right Tribe: The world's longest lived people chose or were born into social circles that supported healthy behaviors. Okinawans created moais, which is a group of 5 friends that committed to each other for life. Framingham Studies showed that habits like smoking, obesity, happiness and loneliness are all contagious. This is why social networking among each other, shapes a healthy behavior.

(Credit-Canva)
“Why Do I Feel Cold All The Time?” Reasons For Low Temperature Tolerance
Just how people have pain tolerance and taste tolerance, some might also have different cold tolerance. Feeling usually cold isn't a sickness itself, but it can signal an underlying health issue. It could be related to your thyroid, the part of your brain that controls temperature (hypothalamus), or how your blood flows. Conditions like anemia, hypothyroidism, fibromyalgia, or anorexia can also cause it.
Cold intolerance means you feel much colder than normal, not just a little chilly. You might complain about being cold when everyone else feels fine, and extra clothes might not help. Sometimes, only certain parts of your body, like your hands, feel very cold.
If you suddenly start feeling unusually cold, and it doesn't go away, see your doctor. They will figure out what's causing it and how to treat it. Here are some reasons why you could be feeling this way.
Dehydration
Your body needs water to stay at the right temperature. If you don't drink enough water, you can feel cold. Water helps your body hold onto heat. If you are dehydrated, you might also feel dizzy, have a dry mouth, and feel tired. To avoid this, drink plenty of water. You can also get water from fruits, vegetables, and soups.
Blood Sugar Conditions
If your blood sugar is too high for a long time, it can hurt the nerves in your hands and feet. This is called peripheral neuropathy. It can make your hands and feet feel numb, painful, and cold. Also, if your blood sugar gets too low, you can feel chills. So, it is important to control your blood sugar. If you have diabetes, see your doctor regularly.
Low Body Weight
If you are very thin, you might feel cold more easily. This is because your body doesn't have enough fat to keep you warm. Your muscles also help make heat. So, if you have low muscle mass you will also feel colder. If you are underweight, make sure you are eating a healthy diet.
Lack of Sleep
When you don't get enough sleep, it can mess up your body's temperature control. This can make you feel cold. Not sleeping enough can also hurt your metabolism. Try to get 7-8 hours of sleep each night. Make sure your bedroom is cool and dark. If you still have trouble sleeping, talk to your doctor.
Anorexia Nervosa
When someone has anorexia, they are very afraid of gaining weight. They might eat very little or exercise too much. This makes their body very thin. Because they have very little body fat, they get cold easily. They may also feel sad, have dry skin, and have trouble thinking. If you think someone has this problem, it is very important to seek out professional help.
Hypothyroidism
Your thyroid is a gland that helps control your body's temperature. If your thyroid doesn't make enough hormones, you can feel cold all the time. This is called hypothyroidism. You might also have dry skin, hair loss, and weight gain. If you have these symptoms, see your doctor. They can give you medicine to help your thyroid.
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron helps your blood carry oxygen. Oxygen helps your body make heat. If you don't have enough iron, you can feel cold. You might also have pale skin, brittle nails, and trouble concentrating. To get more iron, eat foods like beans, chicken, and fish. Your doctor can also give you iron pills.

(Credit-Canva)
Can Your Personality Trait Affect Your Health?
The way you act and certain traits that are unique to you, are what draw people to you. Whether it is the way you talk or meet people, or other mannerisms, your personality has a big part to play in how you are perceived. While your personality obviously has a lot of sway in your social life, there are many other ways it can affect your life.
Having a fun and inviting personality can be a bonus point for your personal and work relationships. People love interacting with you and generally enjoy your company. But could it also be a bonus point for your health? Personality and mental health go hand in hand, and there is research to prove so. Here are some ways ‘good’ personalities benefit you and ‘bad’ one negatively affect your health.
Optimism
If you're optimistic, you tend to see the bright side of life. According to a 2019 study published in PNAS this helps you live healthier and longer. Optimistic people have less inflammation in their bodies and healthier cholesterol. They also take better care of themselves by exercising and eating well. When you're sick, being optimistic helps you cope better and feel less stressed.
Conscientiousness
Being conscientious means you're organized, responsible, and careful. According to a 2013 Health Psychology study, people with this trait often live longer and are healthier. They make good choices, like exercising and eating healthy. They also go to the doctor regularly and follow their advice. This helps them recover faster from illnesses and feel less stressed.
Extroversion
Extroverts love being around people. According to a study published in the 2020 APA PsycNet, this social connection can help lower stress and inflammation. They tend to be more active and happier, which is good for their health. Even if you're shy, having close friends and family can keep you healthy. Staying active, even by yourself, can also help.
Openness to Experience
People who are open to new things are curious and creative. According to Social Psychological and Personality Science 2014 study, they're often happier and handle stress better. This leads to better physical health. Trying new things, like traveling or learning a hobby, can make you more open and improve your well-being.
Agreeableness
Being agreeable means you're kind and helpful. Berkeley Well-Being Institute explains that people with this trait have good relationships and less stress. They also tend to make healthy choices and handle stress well. If you want to be more agreeable, try being more compassionate and listening to others.
Negative Traits and Health Risks
Similar to how positive traits benefit our health, negative traits can trigger many issues. Many of these traits can arise due to mental health issues and you should not hesitate to reach out for help if you are going through them.
Hostility
If you're hostile, you're often angry and unfriendly. This leads to stress and isolation, which is bad for your health. High stress weakens your immune system and increases your risk of heart problems. Learning to control your anger and manage stress can help.
Neuroticism
Neurotic people worry a lot and feel anxious. This can lead to mental health problems and weaken your body. Constant stress from worrying can cause health issues. Learning to relax and think positively can help you feel better.
Emotional Suppression
Hiding your feelings can make you feel stressed and anxious. If you always bottle up your emotions, it can hurt your heart and weaken your immune system. It's important to find healthy ways to express your feelings.
Social Inhibition
If you're shy, you might avoid social situations. This can lead to loneliness and stress, which can cause health problems. Slowly facing your fears and getting help from a therapist can make you feel more comfortable around people.
Self-Centeredness
People who are self-centered only think about themselves. This can lead to loneliness and relationship problems, which cause stress. This stress can hurt your heart and immune system. Trying to be more kind and caring can help you feel better and have better relationships.

(Credit-Canva)
Scientific Speaking! What Happens To Your Body When You Are Sleepwalking?
People have their own unique way of doing things, even sleeping. Having traits like snoring when you are sleeping, talking or mumbling occasionally is normal and not out of the ordinary.
When you sleep, your body is busy fixing itself and getting ready for the next day. Your brain also works to clean up and store memories. But, for some people, a part of the brain that controls movement can turn on while they're still asleep. This is sleepwalking. People who sleepwalk might walk around, talk, and even have their eyes open. They look like they're awake, but they're not.
The Cleveland Clinic explains that if you try to wake them up suddenly, they might get confused or upset. So, it's better to gently guide them back to bed. This helps keep them safe from getting hurt.
Sleepwalking isn't always like you see in movies, with someone walking with their arms out. Sometimes, people do normal things like getting dressed or trying to eat, but they might be clumsy. They could even try to do dangerous things, like drive or climb out a window. What's strange is that they won't remember any of it the next day. It happens during a deep part of sleep. It's considered a sleep problem, like sleep talking. It's important to know that people sleepwalking are not doing it on purpose, and they are not fully aware of what they are doing.
What Causes Sleepwalking, Can You Treat It?
Sometimes, sleepwalking runs in families, so it can be inherited. But it can also happen because of other things. If you don't get enough sleep or if you're really stressed, you might sleepwalk. If you hurt your head, that can also cause it. Drinking alcohol or taking certain medicines can also make it happen. And some sleep problems, like when you stop breathing for a bit while sleeping, can also cause sleepwalking. Kids sleepwalk more often than adults, and usually, they stop doing it when they get older.
If you only sleepwalk once in a while, you probably don't need any special treatment. The most important thing is to make sure your home is safe. Put away sharp things, lock the doors, and close the windows. If you're sleepwalking a lot and it's making you tired during the day or bothering other people, you should see a doctor. They can figure out why you're sleepwalking. They might suggest talking to a therapist to help with stress, or they might give you medicine to help you sleep better. If your medicine is causing it, they might change it. Also, having a good bedtime routine and not drinking alcohol before bed can help.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

