- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
No Washrooms for Women: The Shocking Health Risks of UTI, Hyperuricemia & More

Credits: Unsplash
A report by Swachh Bharat Mission says that 74.5 per cent of public places are equipped with toilets. Another report by the Ministry of Jal Shakti states that there are 2.23 lakh Community Sanitary Complexes built across all States and UTs under the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) since October 2014. Over 92 lakh toilets have been constructed since the launch of SBM Gramin (SBM (G)) in April 2020.
While toilets are there, are they accessible? This is the question one should ask. The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) focuses on 131 health indicators, but not until the NFHS 5 survey did they include the question of accessibility of toilets in the survey. This happened after the inputs from the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) and the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare questioned the accessibility.
One might ask, why is the question of accessibility so important? The answer is quite simple. Access to water, sanitation and hygiene is the most basic human need and is also included under the Sustainable Development Goals by the UN.
Are These Numbers Real?
Just a few weeks back, I was travelling to Himachal Pradesh on a bus. While I was excited to explore the state for the first time, anxiousness gripped me. “What if I have to dehydrate myself again on the journey?” I thought.This thought crossed my mind because back in 2021, I went on a solo trip, on a bus to Udaipur from Delhi. There, the bus made two stoppages. This was done so people could get a quick dinner and freshen up, relieve themselves and be prepared for the rest of the journey. This was a nightmare. The bus only stopped for 10 minutes. While some men used the washroom, others went to the bushes.
For the women, there were three cubicles. One of them was broken, and the other one did not have a light bulb, which meant only one was usable. There was a long queue for that cubicle, and time was short. There was no point in trying to find an isolated corner, because it was past midnight, in an unknown area.
I waited anxiously. When finally, my turn came, I saw an overused, dirty washroom. The toilet seat is in a horrible condition. I wanted to touch nothing there. But I had to pee. So, I used my mask to cover my nose from the odour, folded my pants so they did not touch the floor and squatted. It was quite a task to balance.
On my way back to Delhi, I made sure to not drink any water for over a 13-hour bus journey. I dehydrated myself so I did not have to use the washroom. When I did reach, I was severely dehydrated and was sick for three days.
I shared my experience with my friends only to realise that many women have faced the same. There are no washrooms for women.
A friend of mine told me that it is because these roads and dhabas are mainly designed to serve men. They are the ones who travel at night or are on the roads most of the time. As a result, the few women who do travel or are on the road suffer.
Health Risks Women Are Prone To
Holding your pee for too long can lead to many health risks. But peeing on a dirty seat may lead to infections.Well, it is true, but partially. While holding your pee for too long can lead to health risks, peeing on a dirty toilet seat cannot lead to infections unless your urethra is in contact with the bacteria present on that toilet seat. However, nobody wants to sit on a dirty toilet seat, even if you do not get an infection. A safe and hygienic toilet is a basic need.
One of the regular saleswomen, Usha, who visits my house shared her experience with me. “Being on the road constantly means I must use the dirty public washrooms. But I do not want to use them. So, sometimes I ask my regular customers to let me use their washrooms. Some say yes, and some say no. I understand they are also concerned about their safety and privacy,” she says. As a result, Usha spends most of her day not drinking enough water and holding her pee when she is at work. Due to this, she also suffered from a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI).
Her friend, Halima too faced similar problems and due to increased levels of uric acid in her body, she suffered from Hyperuricemia.
Other health risks are kidney stones and other kidney problems, headaches, dull skin, xerostomia or dry mouth, fatigue, and urinary incontinence, which means losing control over your pelvic floor muscles leading to uncontrolled leakage of urine, seizures and weakness.
What Can You Do?
I learned my lesson from Udaipur and for this trip, I did not want to be sick. So, there are a few essentials that I carried this time with me, that you can too. Because not drinking water or holding your pee is not the solution.Wear comfortable clothes and capris. Capri pants are comfortable and are short in length, which means this won’t touch the toilet floor when you squat or sit.
Carry Essentials
I now carry a stand and pee device. With this device, you no longer must sit on the dirty toilet seat. It is a slanted funnel-like device, which can be placed between your legs when you urinate. Once you are done, you can dispose of it and throw the device in the dustbin.Even though you cannot get a UTI alone from sitting on a toilet seat, it is always safe to carry a toilet seat sanitiser. If nothing, it can help you get rid of the bad odour so you can use your stand and pee device inside the toilet. You can also use disposable toilet seat covers if your knees are weak, and you cannot squat. Always flush with your seat down.
Always keep disposable gloves, a portable bidet (fill it with water before use), a pocket liquid handwash, wet wipes, tissues and sanitiser handy. Do not forget to keep extra sanitary pads. It might sound a lot, but I promise that it all fits in one pouch. Use this travel-friendly pouch every time you are on the road, or using a public washroom.
What Can We Learn From Others?
Countries like South Korea, Japan, and China have incorporated technologies in their toilet to provide a safe experience. They have different water modes, and a button that will wipe your seat when pushed. There are buttons that change your toilet seat covers too.However, in case we do not get these technologically advanced toilets here, you can always pack a travel-friendly toilet kit!
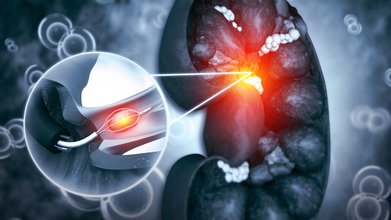
Study shows nanoparticles may shorten kidney stone laser surgeries, reduce recurrence
Credit: iStock
A team of researchers in the US has developed a nanoparticle-based technique that could make laser surgeries for kidney stones faster, safer, and potentially reduce the chances of recurrence.
Engineers from the University of Chicago and doctors from Duke University added dark nanoparticles to a common saline solution used in kidney stone laser surgeries. Their method also promised less recurrence of disease.
The research focused on laser lithotripsy, a widely used surgical method in which lasers are used to break kidney or urinary tract stones into tiny fragments that can then be removed by suctioning or pass naturally.
How Nanofluid Boosts Lasery Surgery
Traditionally, surgeons use a small video-guided laser to fragment the stones. However, achieving effective fragmentation often requires higher laser power, which generates additional heat and causes damage to the surrounding tissues.
Thus the new method “is a way to better utilize the laser energy that is already being employed,” said Po-Chun Hsu, assistant professor at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME).
Hsu noted that their nanoparticle-based “nanofluid” also has the potential to enhance the performance of lasers without increasing power levels. This will effectively fragment the stones and remove the dust particles.
The study, published in the journal Advanced Science, describes an innovative saline solution that enhances the performance of existing laser systems without requiring modifications to the equipment.
By adding dark nanoparticles that absorb laser wavelengths, the solution ensures that more of the laser energy is directed at the kidney stone rather than being reflected or dispersed.
“This improves the amount of laser energy that is transmitted to and absorbed by the stones,” said corresponding author Pei Zhong, a professor of engineering at Duke University.
“Nanofluid introduces a new dimension that can influence this complex physical process, independent of the stone composition or the laser being used,” Zhong said.
Kidney Stone Laser Surgery In 10 Minutes
Laboratory tests using artificial kidney stones showed that the nanofluid increased stone ablation efficiency by between 38 and 727 percent in spot treatments and by 26 to 75 percent in scanning treatments.
The researchers also tested the nanoparticle solution on living cells for up to 24 hours and found it to be non-toxic and safe.
In clinical settings, however, exposure would be much shorter. Laser lithotripsy is typically an outpatient procedure lasting about 30 minutes. The researchers believe that improved laser absorption could reduce the procedure time to around 10 minutes.
“If surgeries take too long, waste heat from the laser can accumulate and cause more harm than the stone removal itself,” Hsu said.
Kidney Stones: Symptoms And Prevention
Kidney stones are hard mineral or acid salt deposits formed in the kidneys. It occurs due to concentrated urine, and causes intense, radiating back/side pain, nausea, and blood in urine.
Common causes include
- dehydration,
- diet,
- obesity,
- family history
- metabolic issues
- staying well-hydrated
- reducing sodium levels
- eating fewer oxalate-rich foods
- consuming sufficient calcium-rich foods
- increasing citrus intake.
Amy Carr, Former England Youth Player Dies At 35

Credits: Instagram
Former youth player of England, Amy Carr dies at the age of 35. England women's football team too paid tribute on her death. Carr was a former goalkeeper who played for England Under-17s and Under-19s. She was diagnosed with a brain tumor for a second time.
She was diagnosed in 2015 and raised more than £2,000 for charity by running the Dublin Marathon in 2024.
"We are heartbroken to hear that former England youth player Amy Carr has passed away aged 35," read a statement on the Lionesses' X account. "Amy, who was diagnosed with a second brain tumour in 2024, devoted her time to raising money for vital brain tumour research that could help others. She remains an inspiration to all."
Carr also played for Arsenal, Chelsea and Reading before she gained a football scholarship in the USA. Chelsea added on X: "We are saddened to learn of the passing of former Chelsea goalkeeper, Amy Carr. Our condolences are with Amy's friends and family at this time."
What Is Brain Tumor?
Before diving into the concept of a brain tumor, it is important to first understand what a tumor is. A tumor refers to an abnormal lump or mass that forms due to the uncontrolled growth of cells in the body.
tumors are broadly classified into two main categories:
- Benign
- Malignant
A benign tumor consists of normal cells that have grown excessively to form a lump. This overgrowth may result from something going wrong in the body, but the cells themselves are not cancerous. On the other hand, a malignant tumor is made up of abnormal cells that grow uncontrollably. These are cancerous cells, and their aggressive nature can lead to serious health issues.
A brain tumor is a condition in which abnormal cells develop within any part of the brain. Similar to tumors elsewhere in the body, brain tumors can also be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The presence of a tumor in the brain can interfere with normal brain function, depending on its size, type, and location.
Our bodies possess a natural healing mechanism that is crucial for survival. This repair system is activated whenever there is damage from injury, radiation from the sun, or harmful chemicals in the environment. However, this process can occasionally go wrong. When it does, small clusters of cancerous cells may begin to form. In most cases, the immune system successfully detects and destroys these abnormal cells before they grow. But in rare instances, these cancerous cells evade immune detection and continue to grow, leading to the formation of tumors or cancers.
Such abnormal growths can occur anywhere in the body. When these growths are located in the brain or spinal cord, they are referred to as Central Nervous System (CNS) tumors.
India Is Home To 25% of the World’s Cervical Cancer Victim

Credits: Canva
India is home to 25 per cent of the world's annual count of cervical cancer fatalities. According to the World Health Organization GLOBOCAN report of 2022, India reports over 120,000 new cases with nearly 80,000 fatalities. This is the highest death-toll worldwide from cervical cancer each year.
In India, a new case is diagnosed every four minutes, and another woman dies approximately every seven minutes. Persistent infection with high-risk HPV strains, especially types 16 and 18, is the leading cause of cervical cancer. Meanwhile, studies show that even a single dose of the HPV vaccine can provide long-lasting, potentially lifelong protection.
To combat this, India launched a nationwide campaign to vaccinate young girl against the human papillomavirus (HPV). This is also the second most common cancer among women in the country. India kicked off the nationwide campaign on 28 February. Prime Minister Narendra Modi at Ajmer city in the western state of Rajasthan inaugurated this campaign. Vaccines were made available free-of-cost at government facilities to approximately 11.5 million girls aged 14 years across the country.
Currently, approximately one in every 50 girls born in India is expected to develop cervical cancer during her lifetime, and widespread vaccination is likely to reduce this risk significantly," said Partha Basu, Head, Early Detection, Prevention & Infections Branch at the International Agency for Research on Cancer.
What Is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer develops in a women's cervix (uterus opening) due to abnormal cell growth, primarily caused by persistent HPV infection, a common infection that's passed through sexual contact.
When exposed to HPV, the body's immune system typically prevents the virus from causing damage however, in a small percentage of people, the virus can survive for years and pave the way for some cervical cells to become cancerous.
Treatment involves surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, with early detection significantly improving outcomes, though it remains a major cancer in low-income countries Cervical cancer can also be prevented through vaccination and regular screening (Pap/HPV tests).
Symptoms Of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer has no symptoms in the early days and therefore, is hard to detect until it has spread. However, the early-stage symptoms include:
- Vaginal bleeding after sex
- Vaginal bleeding post-menopause
- Vaginal bleeding between periods or unusually heavy/long periods
- Watery vaginal discharge with a strong odor or containing blood
- Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse
- Advanced Cervical Cancer Symptoms (when cancer has spread beyond the cervix)
- Painful or difficult bowel movements or rectal bleeding
- Painful or difficult urination or blood in the urine
- Persistent dull backache
- Swelling of the legs
- Pain in the pelvis or lower abdomen
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

