
Credits: Canva
RFK Jr. Plans To Ban Fluoride In Drinking Water Across All U.S. States
Since the Trump administration took over the United States, a lot has changed, especially in the health sector. So, it comes as no surprise that this week, US Health Secretary Robert F Kennedy Jr announced plans to urge the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to stop recommending the addition of fluoride in community water systems across the country. He also noted that the formation of a task force will be dedicated to examining the risk of water fluoridation.
The same day when these plans were announced, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) said that it had been reviewing new scientific findings related to potential health risks from fluoride exposure. Although the EPA does not mandate the use of fluoride, it does set the maximum allowable level of fluoride in public drinking water. At this moment, it is at 4 milligrams per liter.
Kennedy, who spoke in Salt Lake City alongside EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin also praised Utah for taking a bold step. Utah in the previous month, became the first US state to ban fluoride in all public water systems. This new law will come into effect on May 7. Republican Governor Spencer Cox also signed the legislation that not only prohibits fluoridation, but also bars local communities from making their own decisions about it.
Kennedy called Utah a “leader in making America healthy again,” though the move has faced fierce criticism from dentists, scientists, and public health advocates nationwide.
What Is Fluoride And Why Is It Added To Water?
As per the CDC, it is a naturally occurring mineral that, when added in small amounts to water, has been proven to prevent tooth decay. CDC also notes that it helps strengthen tooth enamel by replenishing minerals that are worn away by acids in the mouth.
The origin could be traced back to 1950, when the US had endorsed water fluoridation as a major public health achievement. As per the CDC, 0.7 milligrams of fluoride per liter of water can be added to reduce dental cavities in children and adults alike.
However, over time, there have been concerns have emerged, including excessive fluoride exposure. There have been studies too that looks at the areas with higher-than-recommended fluoride levels. These findings have linked it to the issues such as thyroid disease, arthritis, and lower IQ in children.
A 2024 review published in Science Direct titled Does fluoride exposure affect thyroid function? A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis notes that exposure to high-fluoride drinking water appears to non-linearly affect thyroid function and increase TSH release in children, starting above a threshold of exposure, and to increase the risk of some thyroid diseases.
Another study published in JAMA Pediatrics in 2025, also available on the National Toxicology Program by the US Department of Health and Human Services, finds that higher levels of fluoride exposure, such as drinking water containing more than 1.5 milligrams of fluoride per liter, are associated with lower IQ in children.
However, experts caution that many of these studies are inconclusive or based on levels not commonly found in U.S. water systems.
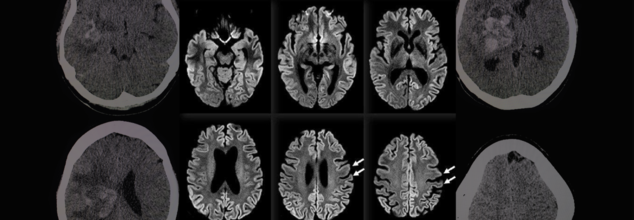
Rare 100% Deadly Brain Disease Kills Two In Oregon County, Third Infection Confirmed
A rare and fatal brain disease with a 100% mortality rate has gripped Hood River County, Oregon, raising concerns within the medical community and eliciting intense probes by local and federal health officials. It is called Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD), and it has killed two people and impacted a third in eight months—a terrifying cluster in a county of only slightly more than 23,000 people.
On April 14, the Hood River County Health Department reported one case of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and two more probable cases. Although only one case has been confirmed by a diagnosis through an autopsy, the other two are presumptive and await post-mortem confirmation through examination of brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid. Such examination, as explained by Trish Elliott, Director of the Hood River County Health Department, may take months.
Although the origins of these three cases are still unknown, the cluster is epidemiologically significant. The U.S. experiences about 350 cases of CJD each year, or 1 to 2 cases per million individuals globally. For Hood River County, with only 23,000 people, to see three cases over such a brief time span is an epidemiologic outlier.
What Is Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)?
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is a rapidly advancing and always lethal neurodegenerative disease resulting from misfolded proteins known as prions. Initially documented in the 1920s by German physicians Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Jakob, CJD causes sponge-like holes to form within the brain, destroying its structure and function.
CJD is a member of the larger family of prion diseases, which also encompasses other rare but fatal disorders like kuru and fatal familial insomnia. Similar to bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly referred to as mad cow disease, CJD irreversibly destroys the brain and has no cure.
CJD Symptoms and Progression
The symptoms of CJD are extreme and worsen quickly. Early symptoms may involve confusion, disorientation, personality changes, memory loss, visual disturbances, and stiffness of the muscles. Later in the disease, patients can develop hallucinations, difficulty speaking or swallowing, seizures, and sudden jerky movements.
Death typically occurs within a year of the onset of symptoms, usually as a result of complications such as pneumonia, heart failure, or problems arising from neurological deterioration such as falls and choking.
Symptoms in the early stages of sporadic CJD usually resemble other dementias but worsen with terrifying rapidity. The majority of individuals with sporadic CJD are between 50 and 80 years of age, but some genetic forms can occur earlier, even in some people as young as 30.
Various Types of CJD
CJD comes in several types:
Sporadic CJD (sCJD): This type is the most prevalent, affecting about 85% of the cases. This type happens spontaneously when healthy proteins in the brain misfolded into prions for unknown reasons.
Genetic CJD (fCJD): Due to mutations in the PRNP gene, this form is inherited and represents about 10–15% of the total cases. The PRNP gene codes for the prion protein (PrP), a protein involved in neuronal communication and protection.
Acquired CJD (also referred to as iatrogenic or variant CJD): This is a rare type that involves outside sources of infection, such as eating infected beef (BSE/mad cow disease) or through tainted medical equipment or transplanted tissue.
In spite of concerns, authorities from Hood River County stressed that the present cases do not seem to have resulted from infected cows. "At this point in time, there is no cause identified between these three cases," the department noted. They also pointed out that CJD cannot be transmitted via air, touching, social contact, or water.
Public Health Measures and Continued Investigations
The Hood River County Health Department, in collaboration with the Oregon Health Authority and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), has launched an "active and ongoing investigation" into the three reported cases.
“We’re trying to look at any common risk factors that might link these cases,” Trish Elliott told The Oregonian. “But it’s pretty hard in some cases to come up with what the real cause is.”
Although risk to the general population is "extremely low," the health department continues to monitor it. Since CJD cannot be definitely diagnosed until after death, real-time monitoring is not easy, and so robust surveillance is essential.
Can CJD Be Prevented?
Although there is no treatment or cure to prevent the development of CJD, the U.S. has established strict public health measures to minimize the risk of acquired CJD, especially through food supply control and medical safety measures.
Federal authorities have maintained since the 1990s a prohibition against feeding cattle which could be contaminated with BSE, and employment of high-risk material in foods is strictly barred. Sterilization processes of surgical devices as well as strict donor screening in transplantation and transfusions are all undertaken to cut back on iatrogenic spread.
While medical officials wait for further verification and possible connections between the three patients, the attention is on education, surveillance, and reassurance to the public.
Although it is reassuringly ominous to witness a disease of this kind emerging in a small American community, the risk at the international level remains low, especially with measures presently in place. Nevertheless, the cases are a sobering reminder of the enigma that prion diseases continue to pose to modern medicine.
Health officials are still keeping an eye on the matter and are asking people not to panic but to remain updated. "The health department will remain vigilant and inform you of any public health risk," officials promised in a statement.
Credits: Canva
World Liver Day: How A Timely Liver Transplant Saved A 30-Year-Old Man
On World Liver Day, which is observed on April 19, to spread awareness about liver health and the life-saving power of organ donation, let us look at one such real-life story. This is where doctor's prompt's action and one's selfless donation saved one human's life.
When the 30-year-old Delhi-based man walked into the hospital, he had yellow eyes and dangerously high liver enzymes. He was admitted in Max Super Speciality Hospital, Patparganj. That moment, he rarely knew that his life was, in fact, hanging by a thread. The man was diagnosed with acute liver failure, which was caused by viral hepatitis. His body was slowly shutting down. The frequency of his body shutting down had increased. The doctors also quickly informed the family. This was the one last hope of survival - a liver transplant.
The First Option Failed
His sister was family's first ray of hope. She was also willing and had a compatible liver whose part of it could be donated. However, pre-surgery tests revealed that her liver size was too small to ensure a safe transplant. The family then proposed the patient's brother-in-law - a second-degree relative, as the next donor. His liver was a better match, but since he was not an immediate blood relative, there had to be special regulatory approvals which were required.
However, the worsening condition of the patients allowed no such time.
The hospital too scrambled to get clearance for the brother-in-law. All this while, the patient suffered a cardiac arrest. The situation turned dire within minutes. Doctors performed CPR to revive him. He was immediately put on ventilator support. The decision had to be taken soon.
A Miraculous Surgery
With no time in hand, the doctors decided to go ahead with the sister as the donor, though there were risks there too.
A team of highly skilled hepatobiliary surgeons, anesthesiologists, and critical care specialists took over. In a high-risk, nine-hour surgery, they removed the patient’s failing liver and replaced it with part of his sister’s.
“This was one of the most challenging cases we’ve handled,” said Dr. Ajitabh Srivastava, Director – HPB Surgery & Liver Transplant. “When the patient collapsed, our team acted within seconds. Every decision, every move mattered. His survival was truly a team triumph.”
The patient is now recovering well.
What Is A Liver Transplant?
As per the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, a liver transplant is a surgical procedure to replace a diseased liver with a healthy one from a donor. It’s often the last resort when liver failure occurs—whether due to chronic illness or sudden injury.
When Is It Needed?
People may need a liver transplant for:
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Fatty liver disease (NASH)
- Cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis C
- Liver cancer with cirrhosis
- Acute liver failure (often due to drug overdose, hepatitis, or toxins)
Types of Liver Transplants
Deceased Donor Transplant:
The most common type, where a full or partial liver is taken from someone who has recently died.
Living Donor Transplant:
A healthy person donates a portion of their liver—typically a close relative. Both the donor’s and recipient’s liver regenerate to normal size in a few weeks.
What Must Be Kept In The Mind?
- Matching and Compatibility: Blood type, liver size, and health are crucial.
- Approval Process: Especially important for non-blood relatives.
- Recovery and Monitoring: Post-op care involves lifelong medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups.

Credits: Canva
Medical Cannabis May Help Fight Cancer, Largest-Ever Study Shows Potential To Treat Symptoms
The largest-ever scientific study on cannabis and cancer has shown strong evidence that medical cannabis can do more than treat symptoms — it could actually fight the disease itself. The research, published in Frontiers in Oncology, provides a robust and data-heavy analysis that brings much-needed clarity to a very contentious issue.
Led by Ryan Castle, Research Director of the Whole Health Oncology Institute, this revolutionary analysis converges more than 10,000 studies — the largest such inquiry into medical cannabis and cancer to date.
Cannabis has been in the middle of medical controversies and legislative wars for a long time. Traditionally, the Schedule I status of cannabis under federal law has limited high-quality human clinical studies, preventing the medical community from reaching a consensus. Castle and his colleagues aimed to change that.
Our aim was to establish the scientific consensus on the issue of medical cannabis, an area that has been long dominated by a war of cherrypicked studies," Castle said.
In order to transcend prejudice, Castle's team took the large-scale, inclusive approach fuelled by AI and sentiment analysis — a process widely employed by natural language processing to determine whether written material portrays a positive, neutral, or negative sentiment. Here, AI analyzed thousands of abstracts and conclusions drawn in scientific literature to determine whether each one stated agreement, neutrality, or doubt in cannabis's applicability to the treatment of cancer and symptom alleviation.
The result? An overwhelming majority of studies presented a positive view, indicating medical cannabis holds therapeutic value not just for symptom relief — such as reducing inflammation and nausea or boosting appetite — but potentially for accelerating apoptosis, the death of cancer cells.
Castle's group examined over 10 times the amount of research examined in any other meta-analysis. Their report stated that roughly 55% of studies indicated a positive relationship between medical cannabis and favorable cancer outcomes with only a few percent reporting adverse effects or none at all.
That percentage — 55% — may seem humble, but with the sheer scale of the data and the scientific conservative tradition in this area, it's telling. "This level of statistical consensus is precisely what we required to start thinking of cannabis as more than an edgy cure-all," Castle wrote.
In addition, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) revealed that 20% to 40% of patients with cancer currently use marijuana products to deal with side effects such as constant pain, chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, and sleeplessness. Still, investigations had fallen behind trend usage rates based on government policy and availability of funds in the past.
It is valuable to place the results of this mega-study in the context of the overall body of cannabis research. Much of what is published is derived from in vitro (test tube) experiments or animal models and not human trials. However, several of these studies have promising results: compounds found in cannabis — particularly cannabinoids such as delta-9 THC, CBD, and CBG — have been shown to inhibit cancer growth, prevent metastasis, and cause cancer cell death in laboratory experiments.
A 2023 Discover Oncology study supported this perspective, reaching the conclusion that multiple cannabinoids reveal "promising potential as anticancer agents by multiple mechanisms." These include curbing tumor expansion, inhibiting cancer cell invasion, and cutting inflammation — which is a documented driver of cancer growth.
In addition, more recent studies have discovered unforeseen advantages in cancer patients who use cannabis. A University of Colorado study reported that patients who consumed marijuana products from licensed dispensaries for a two-week period reported better thinking and cognition, contrary to previous concerns that cannabis would impair mental sharpness in chronic users.
Even with all the encouraging results, Castle and other specialists advise not to consider cannabis a panacea. The available evidence does not indicate that medical cannabis by itself can heal cancer. Rather, its actual strength is in integrative oncology — as an adjunct therapy in addition to standard therapies such as chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy.
This is in agreement with results of a 2019 literature review, which noted that cannabis potentially slows cancer growth and aids improved treatment outcomes, although its effectiveness is highly variable based on cancer type, formulation of cannabinoids, and dose.
One of the significant challenges that persist in holding back development in this arena is the federal classification of cannabis as a Schedule I drug. According to existing U.S. policy, cannabis is listed alongside drugs such as heroin — a designation that presents many legal and bureaucratic hurdles to researchers and healthcare professionals.
In addition, in the Trump era, the National Cancer Institute highlighted marijuana as one of almost two dozen "controversial or high-profile issues" that needed extra clearance prior to publication or research sharing. This culture of fear and repression has only held back the much-needed research into medical cannabis's complete potential.
The biggest-ever analysis of medical cannabis and cancer isn't asserting to have discovered a cure but what they have discovered is a mounting scientific concurrence that medical cannabis should be included in mainstream discussions of cancer treatment. From reducing side effects to having the potential to interfere with cancer cell life cycles, cannabis might have more than just palliation to provide — it might have clinical benefit.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

