- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
How Quitting Smoking Can Quickly Lower Risk Of A-Fib

How Quitting Smoking Can Quickly Lower Risk Of A-Fib
Smokers who make the decision to quit will experience immediate health benefits, including a rapid reduction in their risk of atrial fibrillation (A-Fib), according to new research published in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. The study, conducted by Dr. Gregory Marcus, a cardiologist at the University of California, San Francisco, offers compelling evidence for smokers to quit, showing that it’s never too late to avoid the damaging effects of smoking on heart health.
Dr. Marcus, the senior author of the study, emphasized that A-Fib can be prevented even in individuals who have smoked for years. "The findings provide a compelling new reason to show current smokers that it’s not too late to quit, and that having smoked in the past doesn’t mean you’re ‘destined’ to develop A-Fib," Marcus explained. "Even for the current and longtime smoker, A-Fib can still be avoided."
What is Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)?
A-Fib is a heart condition that affects the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria. When these chambers beat irregularly, blood can pool and form clots, increasing the risk of stroke. Stroke is one of the most serious complications associated with A-Fib, and smoking is known to exacerbate this risk."There’s strong evidence that smoking increases the risk of A-Fib," Marcus said. "But the benefits of quitting smoking have been less certain." With this in mind, his team sought to determine whether quitting could significantly lower a person’s risk of developing A-Fib, or if the risk would remain the same.
The research team analyzed data from over 146,700 current and former smokers, tracking their smoking habits and health over a 12-year period using data from the UK Biobank database. The results were promising: former smokers had a 13% lower risk of developing A-Fib compared to current smokers, while those who quit during the study saw an 18% reduction in their risk.
"This is likely a testament to the potency of reducing atrial fibrillation risk pretty shortly after quitting," Marcus said in a statement from the American College of Cardiology.
The findings highlight the importance of quitting smoking, not only for general health but specifically for reducing the risk of serious heart conditions like A-Fib.
Tips for Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to lower the risk of A-Fib and improve overall heart health. While it can be challenging, the benefits of quitting are clear and immediate. Here are some tips to help you quit smoking successfully:
1. Choose a specific date to quit smoking and stick to it. Prepare yourself mentally and physically for this change.
2. Reach out to family, friends, or a support group to help keep you accountable. Sharing your goals with others can provide encouragement.
3. Options like nicotine patches, gum, or lozenges can help ease withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings.
4. Identify situations that make you want to smoke, such as stress or social gatherings, and find healthy ways to cope with them.
5. Regular exercise can help distract you from cravings and improve your mood during the quitting process.
6. Drinking water can help flush nicotine out of your system faster, reducing cravings.
7. Activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, a common trigger for smoking.
Quitting smoking offers immediate and significant benefits, particularly in reducing the risk of atrial fibrillation. The latest research provides smokers with more motivation to quit, showing that it's never too late to take control of their heart health.
Menstruation Not a Disability: Experts Call Mandatory Period Leaves Unnecessary, Urge Alternative Options

Credit: Canva
Menstruation is not a disability, and therefore, there is no need for mandatory period leaves, said experts, a day after the Supreme Court of India quashed the petition seeking a menstrual leave policy.
The top court expressed concerns that a law making paid leave during menstrual pain compulsory could harm the careers of young women and deprive them of equal opportunities.
While such a policy may look appealing from a “rights perspective,” the court noted it could have “long-term impacts.”
According to the 2025 Periodic Labor Force Survey (PLFS) data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI), women’s labor force participation (LFPR) showed significant growth, reaching 35.3 percent in December 2025, driven largely by a consistent rise in rural areas, which peaked at 40.1 percent.
The female worker population ratio (WPR) also increased, reaching a yearly high in December, highlighting greater engagement in the workforce.
However, India’s female participation remains notably lower than the global average of nearly 49 percent and the OECD average of 67 percent, indicating a persistent, though shrinking, gender gap.
In this context, the court observed that a mandatory period leave policy could create the impression that women “still have some natural issues” and “are not at par with male persons.”
“Will an employer be happy if an employee takes leave every month? You risk creating a situation where employers may be reluctant to hire women,” the bench said.
Period Pain is Real. Paid Leave Unnecessary
HealthandMe spoke to several experts who agreed with the Supreme Court’s view, noting that while period pain and related concerns are real, they do not warrant paid leave for all women employees.
Periods affect women worldwide. For some, it comes with severe back pain, headaches, cramps, fatigue, and other symptoms. For others, the days pass with little discomfort.
“I feel mandatory menstrual leave for all female employees is unnecessary. While menstrual issues are real, not everyone suffers from them. Young women experience debilitating pain in about 1 in 10 cases, while women in their 40s may experience heavier bleeding, perhaps debilitating in 1 out of 7 individuals,” Dr. Ruma Satwik, Senior Consultant at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, told HealthandMe.
Dr. Sabine Kapasi, a public health expert and UN advisor, emphasized that menstrual health deserves significant policy attention.
“But a universal requirement for leave may not be sufficient and is not necessarily the best approach,” she added.
Women have long faced societal and workplace stereotypes, with gender bias evident in wages, hierarchies, and opportunities. A LinkedIn report shows that gender disparity is more pronounced in leadership roles: in 2025, women held only 18 percent of top positions in India, far lower than their overall workforce representation.
“A policy must avoid inadvertently perpetuating gender bias in employment or career advancement,” Kapasi told HealthandMe.
During the Supreme Court hearing, Chief Justice Surya Kant said that with the mandatory menstrual leave law, employers might hesitate to hire women.
“We are creating ‘All Women Teams’ and ‘All Women Service Centers.’ How will they function if such a leave policy is approved? Menstruation is not a disability. It is a biological fact that women have managed over generations,” Indira Murthy, Retired Joint Secretary, Government of India, Advocate, High Court and Supreme Court, and Arbitrator, told HealthandMe.
A Sustained and Flexible Approach
Experts acknowledged the genuine challenges women face during menstruation and suggested alternative measures, including work-from-home arrangements.
Murthy noted that the Supreme Court emphasized voluntary employer initiatives, while also stating that proper institutional arrangements should ensure hygiene and safety for women and children.
“For some women, periods are very uncomfortable. They may be unable to work during these days. Companies can provide flexibility and allow period leaves,” said Dr. Alpna Kansal, President of IMA Ghaziabad.
Kapasi recommended a more sustained approach in workplaces, urging employers to recognize that conditions like endometriosis or severe dysmenorrhea can significantly impact well-being and productivity.
Flexible, stigma-free policies can help women while maintaining workplace fairness.
“Menstrual health awareness, workplace flexibility, access to care, and supportive leave policies integrated into broader occupational health frameworks should be priorities. Women’s health can be safeguarded with a balanced strategy without causing structural disadvantages at work,” Kapasi added.
Dr. Satwik noted that most cases of pain or heavy bleeding can be managed with medication.
“Only in rare cases would symptoms be refractory to treatment, requiring injections or surgical intervention. Those experiencing debilitating symptoms should be granted leave as part of standard sick leave,” she said.
Murthy emphasized that the Supreme Court did not propose a blanket ban.
“No one-size-fits-all policy works. Policy-making should benefit even the last person in the queue. Work-from-home arrangements are a sustainable solution to this issue,” she said.
AHA’s New Dyslipidemia Guidelines Stress Early Screening, Lifestyle Management

Credit: iStock
The American Heart Association (AHA), along with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), today released new guidelines for managing dyslipidemia.
Dyslipidemia can be defined as abnormal levels of one or more types of lipids or lipoproteins in the blood, including cholesterol and triglycerides.
The new guidelines, jointly published in JACC, the flagship journal of ACC, and Circulation, the flagship journal of the AHA, emphasize the need to reduce cardiovascular risk by starting to screen early. It also calls for making lifestyle changes with a proper diet, weight control with exercise, to curb the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
ASCVD is caused by the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries and is the leading cause of death globally.
The guidelines replace the 2018 Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol and offer a comprehensive “one-stop shop”.
Instead of the usual focus on just bad cholesterol, it addresses the need to evaluate, manage, and monitor all dyslipidemias, including high blood cholesterol, hypertriglyceridemia, and elevated lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]).
“While we want to try to optimize healthy lifestyle habits as the first step to lower cholesterol, we realize that if lipid numbers aren’t within the desirable range after a period of lifestyle optimization, we should consider adding lipid-lowering medication earlier than we would have considered 10 years ago,” said Roger S. Blumenthal, chair of the guideline writing committee.
“Lower [LDL-C] for longer, just like lower blood pressure for longer, results in much greater protection against future heart attack and stroke risk,” he added.
What Does The Guideline Say:
1. Early Screening
Early intervention through early screening and healthy lifestyle changes, starting from childhood, is the primary focus of the guidelines. It recommends:
- Children (9-11 years): Cholesterol screening if never done before.
- Adults (30-79 years): Evaluate 10- and 30-year ASCVD risk to determine the need for early intervention
- Considering lipid-lowering therapy for young adults with -- persistent LDL of at least 160 mg/dL, strong family history of ASCVD and/or at least 10 percent 30-year risk for ASCVD
- Family history of heart disease
- Chronic inflammatory diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Metabolic conditions like obesity, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease
- Higher-risk ancestries, including South Asian or Filipino
- Early menopause, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes
- A healthy weight,
- regular physical activity,
- avoiding tobacco,
- healthy sleep habits
- cholesterol-lowering medications
2. LDL-C cholesterol
The guidelines state that individuals with healthy LDL-cholesterol levels or high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), “cannot ‘get out of jail free’ card”. It is important to measure other biomarkers, such as:
- lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)],
- apolipoprotein B (apoB),
- high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP)
- elevated triglycerides
Further, it indicates that LDL-C should be less than
- 100 mg/dL borderline or intermediate risk
- 70 mg/dL for people at high risk
- 55 mg/dL for people at very high risk/need secondary prevention
The guidelines recommend:
- Starting lipid-lowering therapy for people age 40 or older with chronic kidney disease (stage 3 or higher), HIV or Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes
- Continuing lipid-lowering therapy in people being treated for cancer, unless contraindicated
- Deferring most lipid-lowering therapies during conception, pregnancy and lactation
Lauren Macpherson Brushed Off Her Symptoms as ADHD, Turns Out She Had Terminal Brain Cancer
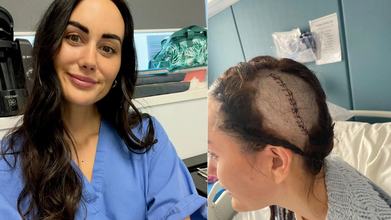
Credits: WNS (The Sun)
Lauren Macpherson, 29, started showing symptoms of what she later realized was terminal brain cancer after a heavy case fell from the luggage rack of a train on her head. She had to be rushed to hospital. She was on the train for a music festival in London and had to be taken off halfway due to excruciating pain. She had instant swelling and doctors feared that she had a fracture in her spine or a concussion. However, scans revealed something else. There was a shadow on her brain, which turned out to be a tumor. She was told that she only had 12 months to live.
“As [the doctor] said it I just knew, because I’ve been having all these symptoms building up, especially over the last two years, and it just clicked. There is an instinct inside you, and when you have been feeling unwell, it just all made sense,” said Lauren.
Lauren Dismissed Her Symptoms As ADHD
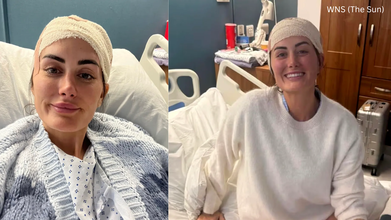
She revealed that she had been suffering from a series of symptoms like extreme fatigue, bad memory, emotional dysregulation, stomach pain, and headaches. She however, believed that these symptoms were linked to ADHD (attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder). This condition is also characterized by behavioral differences like difficulties with focus.
Surprising to most, being told that she had a brain tumor was a "relief" to her. "You think you are going crazy, all these things going wrong. I would have such bad days where I literally could not get out of bed. Like nobody would understand," she said.
Read: Colon Cancer Is The Leading Cause Of Death In US For People Under 50
Doctors had told her in September 2025 that she may have less than a year to live. "I just kept saying, 'just give me my thirties'. I will be grateful for anything just as long as I get my thirties and it gives me time to just say goodbye and have a bit of a life," she said.
“That’s all I could think about. I couldn’t think of anything else, it was just get through it, to get through my thirties and that is all."
The Condition Lauren Has
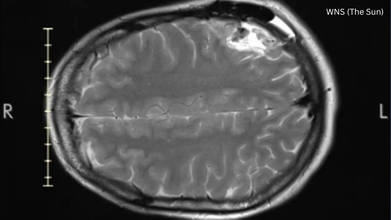
A biopsy showed that she had oligodendroglioma. This is a rare type of tumor that develops in the glial cells. She was told that the average life expectancy of such a tumor is around 10 to 12 years.
Last year, in October, she had a six-hour awake craniotomy at a private clinic in London. While surgeons were able to remove 80 per cent of the tumor, she struggled with memory loss afterwards.
"I couldn’t speak and didn’t even know how to unlock my phone,” she wrote in a blog post for Brain Tumour Research. "Slowly, my memory and speech returned. I still can’t read or write properly and I’m undergoing rehabilitation. I still search for words during conversation and get headaches, but things are improving," she wrote.
She now wants to live her live to full with what time she has left and is planning to marry her partner Zac and enjoy a trip to Italy to mark her 30th birthday.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

