- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Five Common Symptoms Of Stomach Cancer That Should Not Be Ignored
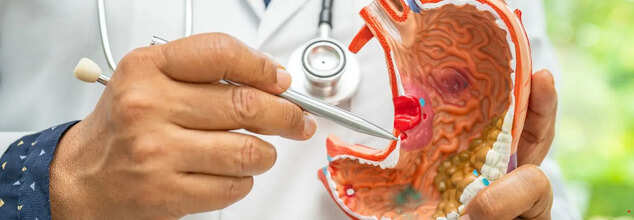
Stomach cancer (credit: canva)
Stomach cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the lining of the stomach. Also, known as Gastric cancer, it affects the elderly more than the adult. According to the American Cancer Society, about 6 of every 10 people diagnosed with stomach cancer each year are 65 or older. Also, the lifetime risk of developing stomach cancer is higher in men (about 1 in 101) than in women (about 1 in 155).
A health expert, speaking to a leading media house, emphasized five common symptoms of stomach cancer that should not be ignored:
1. Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight without trying or experiencing an unexplained drop in appetite, which may signal cancer progression.
2. Pain in the upper part of the abdomen: Persistent or occasional pain in the stomach area, often after eating, can become more severe as the condition progresses.
3. Frequent vomiting after meals: Nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting, may occur especially after meals and is linked to cancer blocking or irritating the stomach.
4. Vomiting blood, which may appear coffee-colored: This can indicate bleeding in the stomach, often caused by ulcers or tumors, and requires immediate medical attention.
5. Black, tarry stools: This occurs when blood from the stomach is digested and passed through the intestines, signaling potential internal bleeding
There are also other concerning signs that should not be overlooked such as jaundice, unexplained weight loss, early onset of diabetes, dark stools, and loss of appetite. Health experts strongly advise seeking immediate medical attention if you notice any of these symptoms. If you or a loved one experience these signs, it's crucial to visit a physician for a thorough evaluation to rule out serious underlying health conditions.
How Does Stomach Cancer Spread?
Oncologist Dr Pankaj Kumar Pande, Director–Surgical Oncology, Max Super Specialty Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, Delhi explained that this form of cancer spreads through three main pathways: Direct spread, lymphatic spread, and bloodstream.
1. Direct Spread: In its early stages, stomach cancer can invade nearby tissues and grow into the deeper layers of the stomach or spread to surrounding organs such as the oesophagus, liver, pancreas, or intestines.
2. Lymphatic Spread: Cancer cells can travel through the lymphatic system. The most common areas affected are the regional lymph nodes near the stomach, particularly those around the liver and diaphragm.
3. Bloodstream: "Cancer cells can enter the bloodstream and travel to distant parts of the body," which is a common route for stomach cancer to metastasize to distant organs.
He further explained that cancerous cells spread from the original tumour to other parts of the body through a process called Metastasis. The most common sites for the spread are the liver, lymph nodes, peritoneum, lungs, bones, and ovaries.
Certain Antibiotics May Alter Gut Microbiome for Up to Eight Years, Study Finds
Credits: Canva
Antibiotics have long been considered lifesaving medicines, especially when it comes to treating serious bacterial infections. However, scientists have also known for years that these drugs can disturb the gut microbiome, the vast community of bacteria that live in our digestive system and play an important role in overall health. Now, new research suggests that the impact of some antibiotics on the gut may last far longer than previously believed.
A recent study has found that certain antibiotics may alter the gut microbiome in ways that persist for up to four to eight years after treatment. The findings were reported by scientists from Sweden and published in the journal Nature Medicine. According to the researchers, these long lasting changes may reduce the diversity of bacteria in the gut, which could potentially influence health over time.
Long term changes in gut bacteria
The gut microbiome contains hundreds of different species of bacteria that help regulate digestion, immunity, metabolism and even aspects of mental health. A healthy gut microbiome usually has a wide variety of bacterial species. When this diversity decreases, it may make the body more vulnerable to several health conditions.
Scientists have previously linked lower microbial diversity in the gut to problems such as obesity, diabetes and inflammatory bowel disease. Because antibiotics kill bacteria to fight infections, they may also eliminate beneficial microbes along with harmful ones. In some cases, this imbalance may take a long time to recover.
In the new study, researchers identified specific antibiotics that appeared to have the strongest and most lasting effects on gut bacteria. These included clindamycin, fluoroquinolones and flucloxacillin. The study’s lead investigator said that these medications were associated with significant changes in the overall composition of the gut microbiome.
Researchers observed that some bacterial species declined after antibiotic exposure while others increased. This shift altered the balance of the microbial community and was linked to reduced diversity.
Comparing antibiotic users and non users
To understand the relationship between antibiotics and gut bacteria, the research team analysed data from Sweden’s National Prescribed Drug Register. They then compared this information with gut microbiome samples from 14,979 adults living in Sweden.
The scientists examined the microbiome of people who had been prescribed different antibiotics and compared it with those who had not received any antibiotics during the same period.
Their analysis revealed that some antibiotics had stronger long term effects than others. For instance, penicillin V, one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for infections outside hospitals in Sweden, appeared to cause shorter lasting changes in gut bacteria.
However, other antibiotics were linked to more persistent shifts in the microbial ecosystem.
Effects that last for years
One of the most striking findings of the study was how long the effects could remain visible. According to the researchers, antibiotic use from four to eight years earlier was still associated with differences in a person’s gut microbiome.
Even a single course of certain antibiotics appeared to leave detectable traces years later. While the exact biological mechanisms are still not fully understood, the researchers believe antibiotics may permanently reshape parts of the microbial community in some individuals.
What this means for future antibiotic use
The researchers believe their findings could help guide future decisions about prescribing antibiotics. If two antibiotics are equally effective against an infection, doctors may eventually consider choosing the one that has a weaker impact on the gut microbiome.
Such insights could help balance the need to treat infections while also protecting long term gut health.
To better understand how the microbiome recovers over time, the scientists are now collecting a second set of gut samples from nearly half of the participants involved in the study. This follow up analysis may reveal how quickly the microbiome can recover after antibiotic exposure and which individuals may be more vulnerable to long lasting disruptions.
FDA Recommends New ‘Subclade K’ Flu Strain for Fall Vaccines

Credits: Canva
A Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advisory committee on Thursday voted to recommend a new strain of flu in its vaccines for fall. This viral strain of flu is called subclade k.
The World Health Organization (WHO) also suggested that the variant is likely one reason flu vaccines were less effective this year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in its Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) noted that influenza vaccine effectiveness was 38 per cent to 41 per cent for preventing outpatient visits for children and adolescents and 41 per cent for preventing hospitalization.
For adults, the number was between 22 per cent to 34 per cent against influenza-associated outpatient visits and 30 per cent against influenza-associated hospitalization.
Although the figures were lower than those seen in recent flu seasons, the CDC emphasized that influenza vaccines still offer meaningful protection and continues to recommend vaccination. Last year alone, flu shots helped prevent around 5 million medical visits, 180,000 hospitalizations, and 12,000 deaths.
According to CDC estimates, influenza caused at least 26 million illnesses, 340,000 hospitalizations, and 21,000 deaths between October 1 and February 28.
At the committee meeting, Dr. Lisa Grohskopf, a medical officer in the CDC’s Influenza Division, noted that subclade K is currently the dominant flu variant circulating in the Northern Hemisphere.
However, the University of Minnesota’s Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy highlighted that flu viruses mutate frequently. This means there is no certainty that the strains chosen now will be the ones circulating in the next flu season. Since vaccine production takes roughly six months, scientists must finalize the formulation as early as February or March.
Arnold Monto, an epidemiologist at the University of Michigan and acting chair of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee, acknowledged the challenge, noting that selecting the right strains involves “a little bit of science and a little bit of luck,” according to Politico.
What Is Subclade K?
Known as the superfly, this is H3N2 'subclade K'. It is a type of seasonal influenza A virus and people have not encountered much of it in the recent years. This is why there is less immunity against it. However, the National Health Service (NHS), UK, has already sent out a 'flu jab SOS' to vulnerable people.
Daniel Elkeles, chief executive of NHS Providers, said that the major concern is that H3N2 is associated with a more severe illness and superflu could be "a very nasty strain of flu". He said that UK could be experiencing a "tidal wave" of illness.
The main strain circulating this winter is a drifted H3N2 variant, which the UKHSA says has left the community with “less natural immunity.” H3N2 strains tend to cause more serious illness in older adults than H1N1 strains and are linked to higher hospitalizations and deaths. This pattern adds further strain to the NHS during the winter months.
India Saw Over 1.5M Cancer Cases In 2025: Which States Are Worst Hit?

Credit: Canva
India has seen a significant rise in the cancer burden, with the cases rising to 1,569,793 in 2025, the government has informed the Parliament.
From more than 1.4 million in 2021, the cancer cases in the country rose to over 144,000 in the last five years, revealed Prataprao Jadhav, Union Minister of State for Health, in a written reply in the Rajya Sabha.
The increase in cases has been consistent:
- 1,426,447 cases in 2021
- 1,461,427 cases in 2022
- 1,496,972 cases in 2023
- 1,533,055 cases in 2024
- 1,569,793 cases in 2025
Similarly, cancer deaths also increased in the country -- 868,588 in 2025 from 789,202 in 2021.
The country reported about 15,000 cancer -related deaths each year:
- 789,202 deaths in 2021
- 808,558 deaths in 2022
- 828,252 deaths in 2023
- 848,266 deaths in 2024
- 868,588 deaths in 2025
Worst-Affected States And Key Reasons
Jadhav informed that bigger states with large populations have seen a major increase in cancer cases and deaths consistently in the last five years.
States with the highest estimated cancer cases in 2025 include:
Uttar Pradesh - 226,125
Bihar - 118,136 cases
West Bengal - 121,639 cases
Maharashtra - 130,465 cases
Rajasthan - 80,628 cases
States with the highest estimated cancer deaths in 2025 include:
Uttar Pradesh - 125,184 deaths
Bihar - 65,571 deaths
West Bengal - 67,093 deaths
Maharashtra - 71,696 deaths
Rajasthan - 44,402 deaths
Major reasons for the rise in cancer burden include:
- environmental factors such as industrial pollution, pesticide exposure,
- contaminated water sources, by pollutants like industrial waste, pesticides, heavy metals, and pharmaceuticals.
“The review provides a critical analysis of the current evidence, summarizing the association of water contamination, including industrial waste, pesticides, and heavy metals, with rectal and colorectal cancer,” Jadhav stated in the Upper House of the Parliament.
Cancer Care Facilities In India
Jadhav further informed that the government is tackling the growing burden by expanding cancer care infrastructure across the country.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has implemented the Strengthening of Tertiary Care Cancer Facilities Scheme, which has approved:
- 19 State Cancer Institutes (SCI)
- 20 Tertiary Care Cancer Centers (TCCC)
Other high-quality comprehensive cancer care facilities in the country include:
- Tata Memorial Centre’s (TMC) six hospitals in Varanasi, Visakhapatnam, New Chandigarh, Guwahati, Sangrur, and Muzaffarpur
- Cancer treatment facilities in all 22 new AIIMS
- Advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) at Jhajjar
- A second campus of Chittaranjan National Cancer Institute in Kolkata
- 297 Day Care Cancer Centers (DCCCs) as promised in the Union Budget 2025-26
- Free essential medicines and diagnostics at public health facilities
- Anti-cancer drugs in the Essential Drugs List at District and Sub-Divisional Hospitals
- Health insurance of Rs. 5 lakh per family annually for secondary and tertiary care under Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PMJAY)
- Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Pharmacies providing access to affordable cancer medicines.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

