
Bird Flu Outbreak: H5N1 Detected In US Dairy Cows And Poultry; How To Avoid Infection
As avian flu cases soar in US livestock, public health organizations call for urgent surveillance and prevention efforts to check the menace of a possible zoonotic pandemic. Highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 has continued to spread throughout the United States, infecting both poultry and cattle now. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has reported more than 1,009 H5N1 detections in 17 states as of April 2025, including new cases in California and Idaho.
For the first time, the virus is sweeping American dairy cattle, a major departure from its normal avian hosts. New outbreaks have also been confirmed in live bird markets in New York and backyard poultry in New Mexico, showing the rapid spread of the virus in commercial and rural areas.
The crisis fuels worldwide alarm, with veterinarians and infectious disease specialists warning that unchecked transmission among mammals could raise the risk of human-to-human spread, potentially igniting a future pandemic.
From Birds to Cows—and Now Humans is There A Dangerous Mutation?
H5N1 has been widely circulating among wild birds for a long time, but the virus's leap to dairy cows in early 2024 was a watershed moment in zoonotic transmission. Infected states' cows showed symptoms like fever, decreased milk yield, coughing, drooling, and lethargy—puzzling symptoms later linked to avian flu.
The experts suspect that the virus is being transmitted through milking machines, especially auto-milkers, that can transfer traces of the virus from one cow to another. The disease has already infected dairy plant workers, with 70 cases reported in the United States, mostly among farmworkers. Most had mild illnesses, but a death did result in Louisiana in a patient who had some underlying conditions.
A total of all states except two reported H5N1 infection in cattle, poultry, or individuals between February 2024 and February 2025.
Delays in Response Is Alarming
Although the threat was serious, federal agencies have moved slowly, critics say. It took the USDA more than a month to require testing of cattle prior to interstate movement and ten months to launch a raw milk testing program. Even today, testing procedures continue to be irregular, with some states testing on a weekly basis and others participating hardly at all.
This delay has attracted ire from virologists and veterinarians who contend that early and forceful action might have contained the spread more effectively, given H5N1's established virulence and pandemic potential.
WHO New Global Surveillance Guidelines Issued
The World Health Organization (WHO) on April 11, 2025, released revised surveillance guidelines for the detection of human infections of H5 avian influenza viruses. These are intended to boost global readiness, facilitate early detection and response, and augment pandemic readiness.
Under WHO's new guidance, nations are required to inform the agency within 24 hours of the occurrence of any laboratory-confirmed human case of a new subtype of the virus. The guidelines also stress data openness and solicit greater surveillance activities, particularly in areas with heightened livestock-human interaction.
Locally, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) still rates the risk to the general population as low since human-to-human transmission has not yet been established. The CDC, however, observes that the virus is undergoing genetic evolution, which poses concern regarding potential mutations in the future that may alter its behavior.
In the meantime, the CDC has provided explicit PPE guidelines for farmworkers, such as respirators and eye protection, to avoid airborne and droplet transmission. The agency is also increasing testing, although difficulties remain due to the large percentage of undocumented farmworkers who will avoid testing for fear of legal consequences.
Is the Food Supply Safe?
Even with the commonality of H5N1 among poultry and cattle, there are no reported infections from the American food supply. The CDC still recommends basic food safety practices to reduce any risk that may exist:
- Cook chicken and eggs to 165°F (73.9°C)
- Ground beef must be cooked to 160°F (71.1°C)
- Whole beef cuts need to be cooked to 145°F (62.8°C)
- Raw milk and milk products that contain it, like unpasteurized cheese or yogurt, are highly not recommended due to their danger not only for bird flu but for other foodborne pathogens, like Listeria.
Is There a Bird Flu Vaccine?
No FDA-approved H5N1 vaccine exists for humans, though five candidate virus strains have been produced for possible use. The U.S. government has purchased 4.8 million doses of an experimental vaccine in preparation for a future outbreak with ongoing human-to-human transmission.
Internationally, Sinergium Biotech in Argentina, in partnership with the WHO, is developing an mRNA-based H5N1 vaccine, based on the successful platform utilized for COVID-19 vaccines. This effort will provide equitable access to low- and middle-income countries, where infrastructure for pandemic preparedness may not be present.
In poultry, although vaccines do exist, they are not commonly used in the U.S. because of export bans by trading partners that refuse to accept imported vaccinated birds.
How to Avoid Bird Flu?
For the general public, the most effective defense against H5N1 is still preventive action. This includes:
- Avoiding contact with ill or dead animals
- Reporting unusual wildlife or livestock deaths to local authorities
- Practicing safe food handling
- Avoiding eating raw or unpasteurized dairy products
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of public awareness, early reporting, and responsible food handling as essential measures to prevent broader transmission.
Credits: Canva
Lowering Your Blood Pressure Levels Could Slash Dementia Risk By 15%—Here’s How
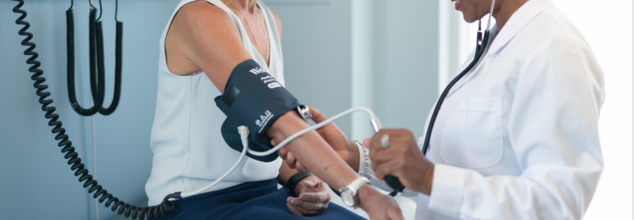
New research brings promising news: lowering your blood pressure could reduce your risk of developing dementia by up to 15%. A large-scale study published in Nature Medicine has spotlighted the significant link between hypertension management and cognitive health—a revelation that could shape public health policies, especially in low- and middle-income countries where dementia rates are projected to climb most dramatically.
Dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, is now the leading cause of death in the UK and one of the fastest-growing health challenges worldwide. According to projections, the number of people living with dementia is expected to rise from 57.4 million in 2019 to a staggering 152.8 million by 2050. With limited treatment options currently available, prevention is becoming the most strategic—and necessary—line of defense. That’s what makes this new research so critical.
The study, led by Dr. Jiang He from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, tracked 33,995 adults over the age of 40 in rural China who had high blood pressure. Participants were divided into two groups. One group received more intensive treatment involving an average of three medications—such as ACE inhibitors, diuretics, or calcium channel blockers—and personalized health coaching to monitor blood pressure at home and adopt lifestyle changes.
The other group, used as the control, received standard care: usually just one medication alongside general advice on healthy living.
After four years, the results were compelling. Those in the more aggressively treated group saw a 15% reduction in dementia diagnoses and a 16% drop in cognitive impairment compared to the control group.
Why Blood Pressure Matters for Brain Health?
While the connection between high blood pressure and cardiovascular events like stroke is well established, its role in cognitive decline has only recently come into sharper focus. Elevated systolic pressure (above 130 mmHg) and diastolic pressure (above 80 mmHg) are now increasingly associated with impaired brain function, memory loss, and dementia.
High blood pressure damages the brain’s delicate blood vessels, leading to reduced oxygen flow, inflammation, and even micro-bleeds—all contributing to structural changes in the brain that accelerate cognitive decline.
This study affirms that blood pressure management doesn’t just protect your heart—it safeguards your brain.
Lifestyle Changes That Make a Difference
What’s particularly encouraging is that the benefits weren’t derived from medication alone. Participants were also coached to:
Lose excess weight
Reduce salt intake
Limit alcohol consumption
Monitor their blood pressure regularly at home
These are simple, sustainable lifestyle interventions that anyone can begin implementing—no matter where they live. In fact, the researchers noted that the benefits of blood pressure control were consistent even in rural, resource-limited communities. This underlines the power of proactive prevention on a global scale.
“For many years, we’ve suspected that high blood pressure was a key risk factor for dementia,” said Dr. Zachary Marcum from the University of Washington in Seattle. “But this study provides some of the most compelling clinical evidence we’ve seen that treating hypertension can significantly lower that risk.”
Dr. Jiang He, lead author of the study, added, “This proven-effective intervention should be widely adopted and scaled up to reduce the global burden of dementia.”
The research not only demonstrates clinical efficacy—it offers a scalable model for other regions battling rising rates of hypertension and dementia, particularly in developing nations.
If you’re over 40, particularly if you’ve been diagnosed with hypertension, the message is clear: now is the time to act. Regular blood pressure monitoring, routine checkups, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can profoundly impact your cognitive future.
This isn’t just about living longer—it’s about living well, with your memory, mental clarity, and independence intact.
Could Microbiome Health Play a Role in Brain Health?
Emerging research has begun to spotlight the intricate link between gut health and brain function—a concept often referred to as the “gut-brain axis.” Scientists are now exploring whether the health of our gut microbiome—the trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms living in the digestive tract—could influence the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, including dementia.
Several studies suggest that gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, may trigger systemic inflammation and compromise the blood-brain barrier, allowing harmful substances to reach the brain and potentially contribute to cognitive decline. Moreover, certain gut microbes are believed to produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play crucial roles in mood regulation, memory, and cognition.
Maintaining a healthy gut through a diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and probiotics could thus indirectly support brain health. While this area of research is still evolving, it adds a fascinating and holistic perspective to the fight against dementia one that goes beyond traditional blood pressure control and delves into the microscopic world of our gut.

Credits: Wikimedia Commons
Pope Francis Passes At 88, After Battling A Long-Term Health Crisis
Pope Francis, the 266th pontiff of the Roman Catholic Church passed away at the age of 88. The Vatican confirmed his passing on Easter Monday, on April 21, 2025, at Casa Santa Marta, his long-time residence in Vatican City.
Cardinal Kevin Farrell in the statement published by the Vatican on its Telegram channel said: "This morning at 7:35 am (0535 GMT) the Bishop of Rome, Francis, returned to the home of the Father."
His death has come just after a month he was discharged from a hospital stay for double pneumonia. This was the latest in string of health challenges that marked his later years.
The Series of Illness and Recovery
Francis, born Jorge Mario Bergoglio in Buenos Aires, Argentina, had battled numerous health issues over the course of his life. His final hospitalization began on February 14. He was admitted to Rome's Agostino Gemelli Polyclinic Hospital. He was diagnosed with bronchitis and his condition worsened and developed into double pneumonia. After 38 days of treatment, he was finally discharged on March 23. However, he passed away a few weeks later.
On the day he was discharged, Archbishop Edgar Peña Parra, the Vatican's chief of staff, visited the pope multiple times during his hospitalization and expressed optimism about his recover. “The pope will recover. The doctors say that he needs some time, but it’s going well progressively,” Peña Parra said.
He earlier showed signs of improvement, however, even then, his recovery was not without its challenges. The Vatican also confirmed that he required rehabilitation therapy to regain his strength, especially when it came to his ability to speak after weeks of using noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
The Vatican also had periodically released health updates, including an audio message recorded from hi hospital bed on March 6. In it, the Pope also thanked people for their prayers and asked for the Virgin Mary's protection. While he was hospitalized, he marked the 12th anniversary of his papacy on March 13. This went along with a quiet celebration and his staff brought him a birthday cake.
However, Pope Francis had a long history of respiratory problems. At 21, he also had a near-death experience from a severe bout of influenza that resulted in part of one lung being removed. This, for him was a life altering experience, he later described in his book Let Us Dream. "for months, I did not know who I was, and whether I would live or die," he wrote, calling it his first real encounter with pain and loneliness.
In June 2021, he underwent colon surgery, and throughout COVID-19 pandemic, he remained cautious, often curbing public engagements. Despite all such setbacks, he kept a demanding schedule well into his 80s.
A Legacy Of Compassion To Continue
Despite his age and ailments, he remained active until the very end. Just a day before his death, he met with the US Vice President JD Vance. On Easter Sunday, while he was too frail to deliver the tradition "Urbi et Orbi" blessing himself, he made a passionate plea through a delegated speech for "freedom of religion, thought, and expression” and condemned rising anti-Semitism and the crisis in Gaza.
Previous updates on Pope Francis' Health, Find Here.

Credits: Canva
Indian-Origin Doctor Found Guilty in Major US Health Care Fraud Case
A federal jury in Pennsylvania found an Indian-origin physician, Neil Anand, 48, guilty of a series of serious charges, which involve healthcare fraud, illegal drug distribution, and money laundering. The conviction was announced by the US Department of Justice on Wednesday. This marks an essential development in a broader effort to crack down on healthcare-related crimes in the United States.
What Exactly Went Down?
Dr Neil Anand was convicted of orchestrating a complex healthcare fraud conspiracy that amounted to $2.3 million. The scheme was the illegal distribution of controlled substances, including oxycodone.
Oxycodone is a powerful and potentially addictive opioid. The drug has also been at the center of the opioid epidemic that has claimed hundreds of lives across the US over the past two decades.
As per the prosecutors, Anand issued a pre-signed prescription for oxycodone, which was then used by unlicensed medical interns to distribute the drugs to nine of his patients. While this is a small number of recipients, the number of tablets distributed is a big one. A total of 20,850 tablets of oxycodone were issued. This is an alarming figure, given that the drug is known for its high risk for addiction.
The "Goody Bags"
It did not just end to prescribed rug abuse, but to fraudulently billing health insurance companies and government insurance plans for "medically unnecessary" prescription medications.
These medications were distributed as a part of what the prosecutors called "Goody Bags". These were packages of various medicines that patients received through pharmacies owned by Anand himself.
These prescriptions were not only unnecessary but were used as a precondition to access the controlled substances. The insurance providers, unaware of the deception, ended up paying a total of $2.3 million for this unneeded drugs. This combination of drug distribution and fraudulent billing is what led to the serious charges of healthcare fraud.
Anand also tried to hide the proceeds from the fraud and transferred $1.2 million into an account under his father's name. He claimed that it was for the benefit of his minor daughter. Authorities saw this as an attempt to launder the money and keep it away from legal scrutiny.
What Is To Be Followed?
This is not the first time Anand has been charged. He was first charged in 2019, along with four other individuals, three of them were his co-defendants and were also reportedly foreign medical graduates who did not possess licenses to practice medicine in the US. He is now awaiting his sentence which is scheduled for August.
One of the prosecutors in the case is Arun Bodapati, an attorney in the Fraud Section of the US Justice Department’s Criminal Division.
Similar Cases
A similar case of a doctor fraud also happened in India. Though, the case did not involve any money laundering it did put a lot of lives at risk. Here, a man posed as UK doctor in India. The man is Narendra Vikramaditya Yadav. He is accused of posing as a British-trained cardiologist and allegedly performing surgeries that led to the deaths of seven of his patients. The 53-year-old used an alias of Dr N John Camm, had been working at a Mission Hospital in Damoh, Madhya Pradesh.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

