- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
This Yoga Breathing Practice Will Relieve Your Stress

(Credit-Canva)
Whenever you are feeling anxious or stressed, the first thing you are told to do is control your breath. There are many different breathing techniques that you can try, like yoga breathing practices like Ujjayi breath, alternate nostril breathing, and deep diaphragmatic breathing.
Diaphragmatic breathing, often called belly breathing, is a simple way to use your diaphragm muscle to breathe more effectively. The Cleveland Clinic explains that the diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle at the bottom of your lungs. When you inhale, it moves down, making space for your lungs to fill with air. Your belly pushes out as this happens. When you exhale, the diaphragm moves up, pushing the air out. This type of breathing is different from chest breathing, where only your chest moves. You can do this breathing technique anywhere, anytime, and no one will even notice. It's a great tool for calming down quickly.
Why Do You Need Breathing Exercises
The reason why this is the go-to response for stressed people is because when you are stressed, your breathing becomes fast paced. The Cleveland clinic explains that stress triggers a fight or flight response in your body. Your body goes into survival mode as it thinks it is in danger. Some symptoms of this include, racing heart rate and blood pressure increase, this means that you are breathing quickly and heavily in order to move nutrients and oxygen into important muscles of your body.
Benefits of Belly Breathing
Belly breathing has many good things about it. It helps calm your nervous system, which is important when you're stressed. It activates a nerve called the vagus nerve, which helps your body relax. When you breathe slowly, your heart rate also slows down, and your body feels less stressed. It helps you control your feelings, like anxiety and fear, so you can think more clearly. This kind of breathing also helps your lungs work better by taking in more oxygen. It can even help you sleep better because it calms your mind. By practicing regularly, you can feel calmer and more relaxed every day.
How to Practice Diaphragmatic Breathing
Certain conditions like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) do make it difficult to work the diaphragm effectively. Your lungs rise and fall naturally, however with COPD air often becomes trapped in your lungs. Make sure you speak to a healthcare professional in case you are facing any difficulties while breathing.
To start, find a comfy spot. You can lie down with your knees bent or sit with your feet flat on the floor. Put one hand on your belly and the other on your chest. Now, breathe in deeply through your nose. Let your belly push out while your chest stays still. Hold your breath for a moment. Then, slowly breathe out through your nose or with your lips a little bit closed, letting your belly go back in. Do this four to six times, slowly and deeply. As you get better at it, you can do more breaths. Practice this every day, even when you're not feeling stressed, to feel calmer all the time.
Can Too Much Running Worsen PCOS? Gabby Logan Opens Up About Athlete Daughter’s Diagnosis

Credits: Instagram
British broadcaster Gabby Logan has revealed that her 20-year-old daughter Lois has been diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal condition that may require her to step back from high-intensity endurance sport, including extreme long-distance running.
Speaking on her Mid-Point podcast, Logan said the diagnosis came after medical consultations about her daughter’s health and training. During the appointment, a specialist advised Lois to avoid “extreme running,” prompting mixed emotions in the family, concern about the condition, but also relief about scaling back punishing physical goals.
What PCOS Means for Athletes
PCOS is one of the most common endocrine disorders in women of reproductive age, affecting an estimated 8–13 per cent globally. It occurs when the body produces higher levels of androgens (male-type hormones) and often involves insulin resistance.
The condition can cause irregular periods, acne, excessive hair growth, weight changes and fertility challenges. Many patients also have difficulty regulating blood sugar, increasing long-term risks of type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
While exercise is widely recommended as a cornerstone of PCOS management, helping improve insulin sensitivity, metabolism and mood, specialists say the type and intensity of exercise matter.
Why Extreme Endurance Could Be A Problem
Doctors cautioned Lois against extreme endurance events such as half-marathons because prolonged, high-intensity training can significantly elevate cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone.
In people with PCOS, hormonal balance is already fragile. Persistently high cortisol may:
- worsen insulin resistance
- disrupt ovulation further
- aggravate fatigue and inflammation
- intensify menstrual irregularities
In other words, although movement is beneficial, chronic physical stress can sometimes counteract the hormonal stability patients are trying to restore.
Moderate-intensity exercise, brisk walking, strength training and shorter runs, is generally considered more supportive for hormone regulation than sustained high-intensity endurance workloads.
From Half Marathon To Shorter Goals
Logan previously completed the London Landmarks Half-Marathon with Lois in 2024, describing the preparation as mentally and physically demanding. The pair had hoped to repeat the experience, but the new medical advice has changed those plans.
Instead, they now intend to focus on shorter runs together.
The television presenter admitted she felt a surprising sense of relief at the specialist’s recommendation, recalling how intense the training had been for both of them.
A sporting life continues — just differently
Lois, a competitive showjumper and university student, has long balanced academics with elite sport. She has ridden horses since childhood and competed at national levels, later even participating in a charity jockey race — an experience she described as “brutal.”
Her diagnosis does not end her athletic pursuits, but it reshapes them.
Medical experts increasingly stress that PCOS management is not about stopping exercise but tailoring it. Sustainable training, adequate recovery, and balanced nutrition often produce better long-term hormonal outcomes than relentless endurance performance.
For athletes with PCOS, the goal shifts from pushing physical limits to supporting physiological stability — a change that, doctors say, can ultimately protect both performance and health.
Are Abs And Core The Same Thing?

Credits: Canva
You must have heard people say, "Tighten those abs!' "Engage you core!" However, have you ever wondered what it really means? Are they the same thing? Is there a difference?
While "abs" and "core" tend to be used synonymously, the reality is that one is simply the exposed tip of the iceberg and the other, a dynamo driving your whole body's power and stability. Whether you're after a six-pack or just want to move with less pain and more power, knowing how your abs differ from your core might entirely overhaul how and why you train.
Although these terms are thrown about as if synonymous, they literally address different muscle groups with redundant but unique functions. And understanding the distinction might change how you train entirely not only for looks, but for functionality, posture, and strength in general.
You must have heard people say, "Tighten those abs!' "Engage you core!" However, have you ever wondered what it really means? Are they the same thing? Is there a difference?
While "abs" and "core" tend to be used synonymously, the reality is that one is simply the exposed tip of the iceberg and the other, a dynamo driving your whole body's power and stability. Whether you're after a six-pack or just want to move with less pain and more power, knowing how your abs differ from your core might entirely overhaul how and why you train.
Although these terms are thrown about as if synonymous, they literally address different muscle groups with redundant but unique functions. And understanding the distinction might change how you train entirely not only for looks, but for functionality, posture, and strength in general.
Abs vs. Core: What's the Real Difference?
Most everyone has an idea of what abs are when they hear the term, it's all about that coveted "six-pack." But abdominal muscles are more than vanity points.
These are the rectus abdominis (for the six-pack appearance), the external obliques and internal obliques (for side bending and twisting), the transversus abdominis (lowermost layer stabilizing the spine), and the pyramidalis (a small muscle located close to the pubic bone).
Found in the front of your body, these muscles assist in the protection of internal organs, aid in posture, and create forward bending and twisting actions.
Visualize your core as the inner strength system of your body. It's not just the abs a larger, more comprehensive area that encompasses pelvic floor, diaphragm, back extensors, obliques, and even hip flexors. The core stabilizes your entire trunk, supports your spine, and facilitates coordinated movement. Whether lifting groceries or marathoning, your core provides balance and injury protection.
So while abs are part of your core, a solid core is so much more than toned midlines—it's your body's anchor.
Why Engaging Your Core Matters More?
If you’ve ever heard a trainer say “engage your core” and wondered what it really means, here’s the truth: core engagement isn’t just about tensing your stomach. It's about bracing your midsection in a way that stabilizes your spine without holding your breath or excessively sucking in.
Done right, activating your core during workouts:
- Reduces strain on the lower back
- Protects joints and ligaments from injury
- Improves posture and balance
- Improves control and efficiency in movement
Most individuals unconsciously overcompensate by hinging backward at the hips or holding their breath—errors that can diminish the efficiency of a workout as well as heighten the risk of injury.
Pro tip: You ought to be able to breathe naturally while keeping a solid, braced core.
5 Highly Effective Ab Exercises
When exercising specifically for the abs, these exercises isolate the front abdominal wall and obliques:
Bicycle Crunches
One of the best exercises to work both the obliques and rectus abdominis. Lie on back, legs up to tabletop, and rotate opposite elbow to knee in pedaling motion.
Leg Raises
Works lower abs. Lie on your back, hands under your hips, and lift legs up to 90 degrees slowly, then return without contact with floor.
Russian Twists
Ideal for the obliques. Sit, lean back somewhat, raise feet (optional), and twist torso side to side holding a weight or medicine ball.
Reverse Crunches
Begin on your back, knees bent. Contract abs in order to lift hips off the ground while curling knees toward your chest.
Flutter Kicks
Lie on your back, raise both legs off the floor a few inches, and alternate kicking up and down. Keep your core tight the entire time.
These exercises are best for developing definition and endurance in your abdominal muscles—but don't begin and end there.
5 Highly Effective Core Exercises
To get your entire core stronger, from back to hips to pelvic floor, these compound exercises are the key:
Plank Variations
From forearm to side planks, this isometric exercise uses every muscle in the core. Maintain hips level, spine neutral, and core braced.
Dead Bugs
Lie on back with arms and legs up. Lower opposite leg and arm slowly while keeping back flat. Works deep stabilizers.
Bird-Dog
On hands and knees, reach out opposite arm and leg. Great legs, lower back, and core stability exercise.
Glute Bridge with March
Lift hips up into a bridge, then alternate marching one foot at a time. Targets glutes, core, legs, and pelvic stabilizers.
Pallof Press
With a resistance cable or band, press hands straight out from chest resisting twisting. One strong anti-twist core exercise.
These training methods cause your body to function as a functional unit. Outcome? Less injury, improved posture, and enhanced performance in sports and everyday activity.
Should You Train Abs and Core Separately?
It all depends on your aim. If your main target is visual definition, ab-specific training along with proper nutrition and cardio is the priority. But for overall strength and spine development, incorporating core exercises into your regimen is not negotiable.
Your ideal weekly training schedule should have a balanced combination of both isolated ab exercises and compound core exercises. Isolated ab movements support the development of muscular endurance and play a role in visible muscle definition, especially in the rectus abdominis—the traditional "six-pack" muscle.
At the same time, compound core training addresses deeper stabilizing muscles that translate to overall strength, mobility, and spinal stability.
This integrated training not only enhances gym performance but also prepares your body to execute daily movement with more ease and efficiency. Knowing the distinction between abs and the core changes the way you train. It's not all about crunches—it's about developing a strong, functional center that stabilizes your whole body.
When you train for more than just looks and with core integrity, you minimize injury risk, enhance athletic performance, and feel stronger in day-to-day movements. So the next time you roll out on the mat, remember: engaging your abs is awesome, but strengthening your core? That's how you fuel your life.
Your Gym Weights Have More Bacteria Than A Toilet Seat
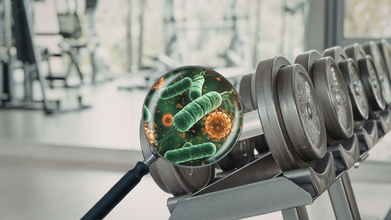
Credits: Canva
We walk into gyms thinking about gains. Stronger muscles, better stamina, maybe even that perfect mirror selfie. Everything looks clean, polished, and professional. But beneath that shiny surface lies an uncomfortable truth.
Studies reveal something alarming. Dumbbells can harbor 362 times more bacteria than a toilet seat, while fitness bikes may carry 39 times more bacteria than restaurant self-service trays. It sounds shocking, but the numbers tell a clear story. Your workout zone might also be a microbial playground.
Why Gyms Become Bacteria Hotspots
Gyms create the perfect environment for germs to thrive. Think about sweat, shared equipment, warm temperatures, humidity, and dozens of people rotating through the same machines every day.
Every time someone grips a dumbbell, lies on a mat, or adjusts a treadmill setting, they leave behind sweat, skin cells, and natural body oils. Multiply that by multiple users in just a few hours, and you have an invisible layer of bacteria building up.
Dr. Susheela Chaurasia, Consultant Microbiologist at Wockhardt Hospital, explains that gym equipment has several small crevices and surfaces that trap moisture and organic material. These warm and moist conditions create an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Among the most common culprits found in gyms are Staphylococcus aureus, commonly known as staph, which causes skin infections, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which thrives in damp areas like locker rooms and can trigger respiratory or urinary tract infections.
Even with routine cleaning, high-touch surfaces remain vulnerable because equipment is constantly being reused.
When Workouts Come With Unwanted Side Effects
Have you ever returned home from the gym with an unexplained rash or irritation? It may not just be coincidence.
When you exercise, your pores open up and your immune system temporarily shifts focus. This can make it easier for bacteria to enter through tiny cuts, abrasions, or hair follicles. Wearing damp gym clothes for too long can also encourage fungal infections and skin irritation.
Frequent exposure to contaminated surfaces may increase the risk of recurring skin conditions, joint infections, or respiratory issues, especially in people with lower immunity.
It is not just gym members who are exposed. Trainers, staff, and cleaning crews operate in the same microbial environment daily. This increases the possibility of bacteria circulating within the space.
Read: Fact Check: Is Weight Lifting Safe for Teens?
Hygiene Is Your First Line of Defense
The good news is that you do not need to cancel your membership. You just need to be more mindful about hygiene.
Start with simple habits. Always wipe equipment before and after use. Use your own towel or mat to create a barrier between your skin and shared surfaces. Avoid touching your face during workouts. Wash your hands thoroughly once you are done. Change out of sweaty clothes immediately after exercising.
Experts stress that disinfection is more effective than basic sanitization when it comes to gym equipment. Non-porous surfaces like metal and plastic should be cleaned with recommended disinfectants because bacteria can survive in cracks or poorly cleaned areas.
Also, avoid walking barefoot in locker rooms, steam rooms, or pool areas, since these spaces are prone to fungal growth.
Do Not Bring the Gym Home
Your hygiene routine should not end when you leave the gym. Shoes worn outdoors and inside the facility can transfer germs onto your home floors. Keeping gym shoes separate or leaving them near the entrance can reduce this risk.
Shower soon after workouts, wash gym clothes regularly, and keep any cuts or wounds covered while exercising.
A Shared Space Means Shared Responsibility
Gyms are community spaces. Hygiene is not just personal but collective.
If you are feeling unwell, skipping a workout might actually be the healthier decision for everyone. Fitness is built through consistency, recovery, hydration, sleep, and balanced habits.
So the next time you pick up those weights, wipe them down first. Staying fit should never mean exposing yourself to unnecessary infections.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

