- Health Conditions A-Z
- Health & Wellness
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Health News
- Ayurveda
- Videos
- Medicine A-Z
- Parenting
Posture Correction: How To Align Your Body For Better Health And Confidence

How To Align Your Body For Better Health
Good posture is more than just standing tall; it’s a crucial aspect of overall health and well-being. Proper alignment of the body can prevent pain, improve physical performance, and boost confidence.
Good posture involves maintaining the natural curves of the spine: the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), and lumbar (lower back) curves. When these curves are in their natural alignment, the muscles surrounding the spine are balanced and support the body effectively.
Benefits of Good Posture
Reduced Back Pain: Poor posture can lead to chronic back pain by putting undue stress on the spine and surrounding muscles. Correcting your posture helps distribute weight evenly, reducing strain on the back.
Fewer Headaches: Tension headaches often stem from poor posture, particularly from slouching, which increases muscle tension in the neck.
Improved Breathing: Proper posture allows the diaphragm to move more freely, enhancing lung capacity and improving breathing.
Enhanced Digestion: Sitting or standing correctly can aid in better digestion by preventing compression of the abdominal organs.
Increased Confidence: Standing tall with good posture can boost your self-esteem and make you appear more confident.
In Vedic traditions, posture is not only about physical alignment but also about spiritual and mental well-being.
According to Ayurveda, good posture facilitates the free flow of prana (life energy) throughout the body. When the spine is aligned, energy channels (nadis) are open, promoting overall vitality and health.
Mental Clarity: The Bhagavad Gita emphasizes the importance of sitting with a straight spine during meditation to achieve mental clarity and focus. This posture helps in maintaining a calm and centered mind.
Spiritual Connection: In yoga, maintaining good posture is essential for spiritual practices. Asanas such as parvatasana, padmasana, vrikshasana etc.are designed to prepare the body for meditation by ensuring that the spine is straight and the body is relaxed.
Here are some tips for maintaining a good posture
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, and weight evenly distributed. Keep your shoulders back and relaxed, and your head level, with your ears aligned over your shoulders.
- Sit with your back straight and shoulders back. Your buttocks should touch the back of your chair. Keep your feet flat on the floor and avoid crossing your legs.
- Use a mattress that supports the natural curve of your spine. Avoid sleeping on your stomach, as it can cause neck strain. Instead, sleep on your back or side with a pillow between your knees.
A few exercises to improve your posture are
Bridges: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Lift your hips by engaging your core and gluteal muscles. Hold for a few seconds, then lower back down.
Planks: Get into a push-up position but rest on your forearms. Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels. Hold this position to strengthen your core, shoulders, and back
Chin Tucks: Sit or stand with your back straight. Pull your chin back towards your neck, creating a double chin. Hold for a few seconds and release. This exercise strengthens the neck muscles and improves alignment.
Move Frequently: Avoid staying in one position for too long. Take breaks every 20-30 minutes to stretch and move around.
Adjust Your Workspace: Ensure your desk and chair are at the correct height. Your computer screen should be at eye level to prevent neck strain.
Mind Your Posture: Regularly check your posture throughout the day. Use reminders or apps to help you maintain good posture habits.
By incorporating these tips and exercises into your daily routine, you can improve your posture, reduce pain, and enhance your overall health and confidence.
Remember, good posture is a lifelong commitment, but the benefits are well worth the effort.
So sit and stand tall, live long !!
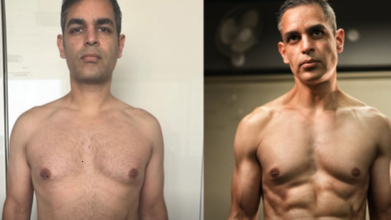
3Ts That Helped Ankur Warikoo Achieve Only 13% Body Fat At 45
Credits: Instagram
Ankur Warikoo, entrepreneur, who has gained fame with his to-the-point practical and solution oriented videos on Instagram, recently talked about his fitness journey and diet routine which helped him achieve only 13 per cent body fat at the age of 45. "The exact method that got me 13 per cent at the age of 45. No steroids, no shortcuts, not AI. The 3T formula got me here, starting with the one most people skip," said Warikoo in his Instagram post.
What Are The 3Ts That Helped Ankur Warikoo Achieve Only 13 per cent fat at 45?
“The only way to lose fat is through a calorie deficit (consume fewer calories than you burn). Many track their calorie-out (how much they burn, through a smart watch or ring). But very few track their calorie-in (how much they eat),” he said.
This is why, T-1 is Track. This phase aims at tracking what you eat and keeping a check on your calorie intake.
Warikoo said that he brough his calorie intake to 1,600 to 1,800. He started with a 500 calorie deficit every day and continued till 7,500 every two weeks to lose 1 kg. Then repeated the same routine. He also increased his protein intake. In a deficit, you lose muscle and fat. Protein replenishes the muscle. Without it, you just end up skinny,” he said.
What His Diet Looked Like
9.30 am – 1 scoop whey protein, creatine, 1 walnut, 4 almonds, 4 cashews, 5-6 raisins
11 am – 200 grams paneer/tofu/tempeh/ or dal chilla. Rarely eggs
1 pm – Fruit
4 pm – 2 rotis (emmer wheat/jowar/soya bean) sabzi+ dal+ low fat yogurt
6.30 pm – 1 scoop whey protein with curd
“I didn’t cut out chhole bhature (my favourite). Had mithai – quite often. The goal wasn’t perfection. It was to reach the two-week deficit,” said Warikoo.
The Second T is for Training
Warikoo's training schedule looked like this:
Tennis – 6 days a week, 1 hour (cardio sorted)
Weights – 6 days a week, 45 minutes
Every day: 2 exercises * 3 body parts = 6 exercises
10-12 reps
3 sets
“Didn’t get bored,” he shared.
The 3rd T stands for Transformation
He said he tracked his daily weight and weekly measurements to document his transformation and the progress he had been making. He said that he also "sent pictures to my trainer for accountability. Ate mostly the same meals. Boring works," he said.
What Do Experts Say?
Experts have noted that a diet, especially like Warikoo's which is mostly vegetarian, excels in sustainability. Furthermore, his diet was balanced with protein, macros from dal, tofu and Greek yogurt. He also did resistance training to preserve lean mass which is a common mid-age related condition that could lead to sarcopenia.
Experts also point out that while tracking weight and measures are great notifiers of tracking health, one should understand that losing weight is not everything. This is why getting blood work at frequent intervals could tell you more than your dropping weight.
India For The First Time Has Guidelines On Muscle Loss
Credits: Canva
Mobility and independence are two things that keep people healthy, however, with age, as bones weaken and muscle is lost, elderly become more dependent. This condition is called sarcopenia, or age-related muscle loss. India is finally focusing on this and have now new guidelines to warn people against it.
The Geriatric Society of India released country's first 'Indian Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Sarcopenia'. These guidelines are a combination of recommendations by experts across multiple specialties, including geriatric medicine, orthopedics, endocrinology, physiotherapy and nutrition. These guidelines aim to help doctors detect and treat muscle loss early. The aim is to not let elderly compromise with their independence.
Also Read: Bruce Willis Health Update: His Death News Is A Hoax; 'He's Still Alive And Well'
What Is Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia literally translates to 'loss of flesh'. Medically, it refers to gradual decline in muscle mass, strength and physical function with aging. While it is often overlooked, it is also the major reason for many fractures and hospitalizations of older adults, and sometimes, even death.
India is expected to have around 319 million people aged over 60 by 2050, which is one-fifth of the population. It could be concerning as they are at risk of sarcopenia. Studies have also shown that the number has increased from 8-18 per cent to 25-40 per cent adults, especially hospitalization cases. Experts point out that those with chronic diseases like diabetes are at a higher risk.
What Are The First Indian Guidelines On Muscle Loss or Sarcopenia?
Dr OP Sharma, who led guidelines said that muscle health is most important for healthy aging. "Strength preserves dignity. Early detection saves independence," he said. Dr Sharma also noted that the sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition and chronic illnesses are accelerating this condition among seniors.
The guidelines also advise doctors to look for warning signs in patients, which include weak grip strength, slower walking speed, or difficulty getting up from a chair. There are also screening tools like SARC-F questionnaire, which could help identify those at risk.
The ray of hope here is that sarcopenia could be prevented or slowed that too with simple lifestyle changes.
What Lifestyle Changes Could Prevent Sarcopenia?
- Strength training exercises
- Adequate protein consumption
- Correcting deficiency including vitamin D and calcium
Doctors are also advising to eat a balanced diet, which includes protein, fats, green vegetables, and pulses. Dr Raju Vaishya of Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals said, "India is a sarcopenic nation". He pointed that everyone needs to be aware about muscle health, however this awareness remains low in the country.
Dr Randeep Guleria said the guidelines aim to brings muscle health into routine medical care. "They bridge science with clinical wisdom, making sarcopenia visible in everyday practice."
Can Just 10 Minutes of Exercise Reduce Depression?

Credit: Canva
A new Nature Human Behaviour (2026) study suggests that single-session psychological exercises lasting less than 10 minutes can lead to measurable decreases in depression symptoms even one month later.
Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders in the world. Every year, hundreds of millions of people suffer from depression, and many are unable to get therapy because of cost, stigma and the dearth of mental-health professionals.
Symptoms include excessive sadness, depression often includes fatigue, changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating and feelings of hopelessness. Treatment requires professional guidance for diagnosis and management.
A 10-Minute Intervention With Lasting Effects
Researchers conducted one of the largest randomized controlled trials testing short mental-health exercises and recruited 7,505 adults in the United States who were suffering from symptoms of depression and randomly assigned them to one of several short digital interventions or to a control group.All the brief interventions took less than 10 minutes to complete and were designed to teach practical coping skills that are commonly used in psychotherapy. Some exercises helped participants to reframe negative thoughts, while others focused on motivation, goal-setting or making sense of things by helping others. Participants completed surveys measuring their well-being immediately after the session and again one month later.
The results were striking: while many exercises boosted motivation and hope immediately, two interventions - Interactive Cognitive Reappraisal and Finding Focus - showed measurable reductions in depression symptoms even after a month. On average, participants experienced about a four percent greater reduction in depression scores compared with the control group.
Although the improvement may appear small, researchers note that brief, scalable interventions could reach millions of people who currently lack access to mental-health care as they can be completed in a few minutes and delivered online, these exercises may allow people to take initial steps toward better mental health, especially those waiting for professional help or unwilling to ask for help.
The scientists also stressed that these activities are not intended to substitute for therapy, but should be seen as readily available tools to help with emotional health.
Exercise and Mental Health: A Growing Body of Evidence
Previous research also shows that a quick burst of activity can make you feel better from other research too. A British Journal of Health Psychology 2024 study found that just 10 minutes of daily mindfulness practice significantly improved well-being and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety among more than 1,200 participants from 91 countries.
Similarly, the US National Institutes of Health (2019) reviews suggest that the physical activity itself may help improve mood and depressive symptoms, strengthening the relationship between movement and mental health.
Collectively, these findings suggest that even small doses of mental or physical activity may lead to psychological benefits.
A Small Step That Can Make a Difference
Depression can make people feel trapped and out of control. The good news of the new research is that it suggests that big changes aren’t always necessary to move forward.
Sometimes, doing a small task, like spending 10 minutes learning a new coping skill or doing a quick mental exercise, is enough to change the way you think and gradually improve mood.
As researchers investigate these brief interventions, one thing is becoming clear: when it comes to mental health, few minutes matter more than we think.
© 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Company Limited

